Overview
The article highlights the seven essential IT compliance frameworks that banking IT managers must grasp to adeptly navigate regulatory obligations and bolster data security. It asserts that frameworks such as ISO 27001, NIST, and PCI DSS are not merely legal requirements; they are pivotal in safeguarding sensitive information and fostering consumer trust. These frameworks empower organizations to mitigate risks related to data breaches and regulatory non-compliance, ultimately enhancing their operational integrity. Are you prepared to integrate these frameworks into your compliance strategy?
Introduction
In the intricate world of banking, where regulations are as dynamic as the technology that supports them, understanding IT compliance frameworks is not merely beneficial—it is essential. These structured guidelines serve as a roadmap for organizations striving to meet legal obligations while safeguarding sensitive data from the myriad threats that loom in the digital landscape.
As financial institutions grapple with the increasing complexity of compliance requirements, the significance of frameworks such as ISO standards and NIST guidelines becomes ever more pronounced. Furthermore, statistics reveal a growing specialization in compliance roles and an urgent need to stay updated on evolving regulations.
Banking IT managers must prioritize these frameworks, not only to protect their organizations but also to enhance their operational resilience and reputation in a fiercely competitive market.
Understanding IT Compliance Frameworks: A Primer
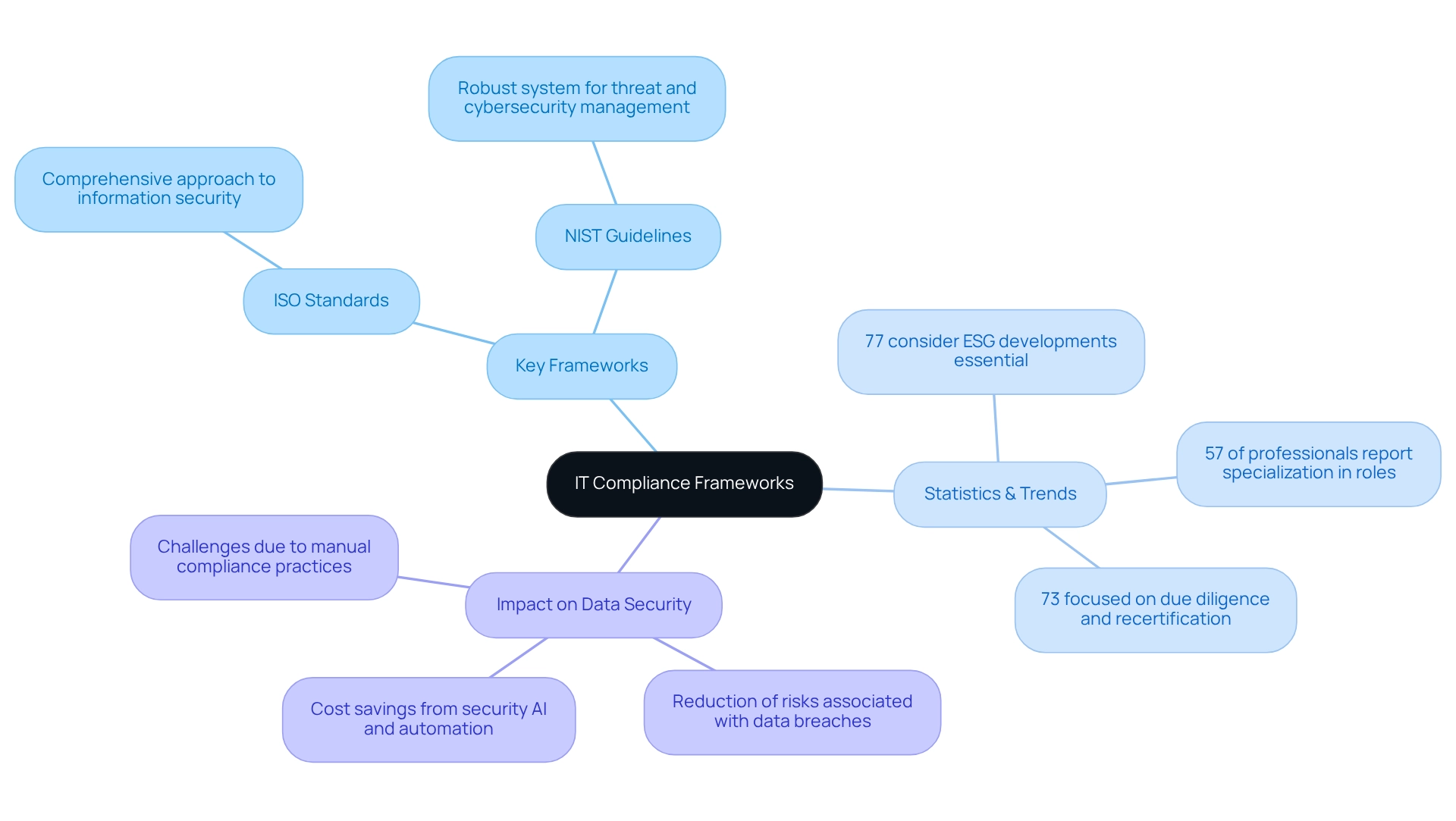
IT compliance frameworks are essential organized collections of instructions that organizations must adhere to in order to meet legal and regulatory obligations. This is particularly critical in the banking sector, where stringent regulations govern operations and data management. For IT leaders, a profound understanding of these frameworks is vital for successfully navigating the complex regulatory landscape.
Key frameworks include:
- ISO standards, which provide a comprehensive approach to managing information security.
- NIST guidelines, which offer a robust system for threat and cybersecurity management.
These frameworks not only assist organizations in mitigating regulatory risks but also play a crucial role in supporting IT compliance structures that protect sensitive information from breaches and cyberattacks.
Recent statistics underscore the growing specialization within regulatory roles, with 57% of corporate risk and regulatory professionals reporting that their responsibilities have become more focused. This trend emphasizes the necessity for financial IT managers to remain updated on the latest developments in IT compliance frameworks. In fact, 77% of these professionals consider it essential to stay informed about the latest Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) advancements, reflecting the evolving nature of regulatory requirements.
Moreover, the impact of IT compliance frameworks on data security in banking is substantial. Organizations that effectively implement IT compliance frameworks can significantly reduce the risks associated with data breaches, which have been shown to lead to considerable financial losses and legal repercussions. For instance, organizations utilizing security AI and automation have reported notable decreases in breach-related costs, highlighting the effectiveness of modern regulatory practices.
Importantly, 73% of risk identification efforts are dedicated to due diligence and recertification, underscoring the significance of thorough compliance procedures in banking.
Incorporating tools such as Zluri’s access review solution can further streamline compliance processes and enhance risk management initiatives. As the landscape of IT regulations continues to evolve, financial IT managers must prioritize IT compliance frameworks to ensure their organizations not only meet regulatory standards but also safeguard their data and maintain a competitive edge in the industry.
The Importance of Compliance Frameworks in Banking
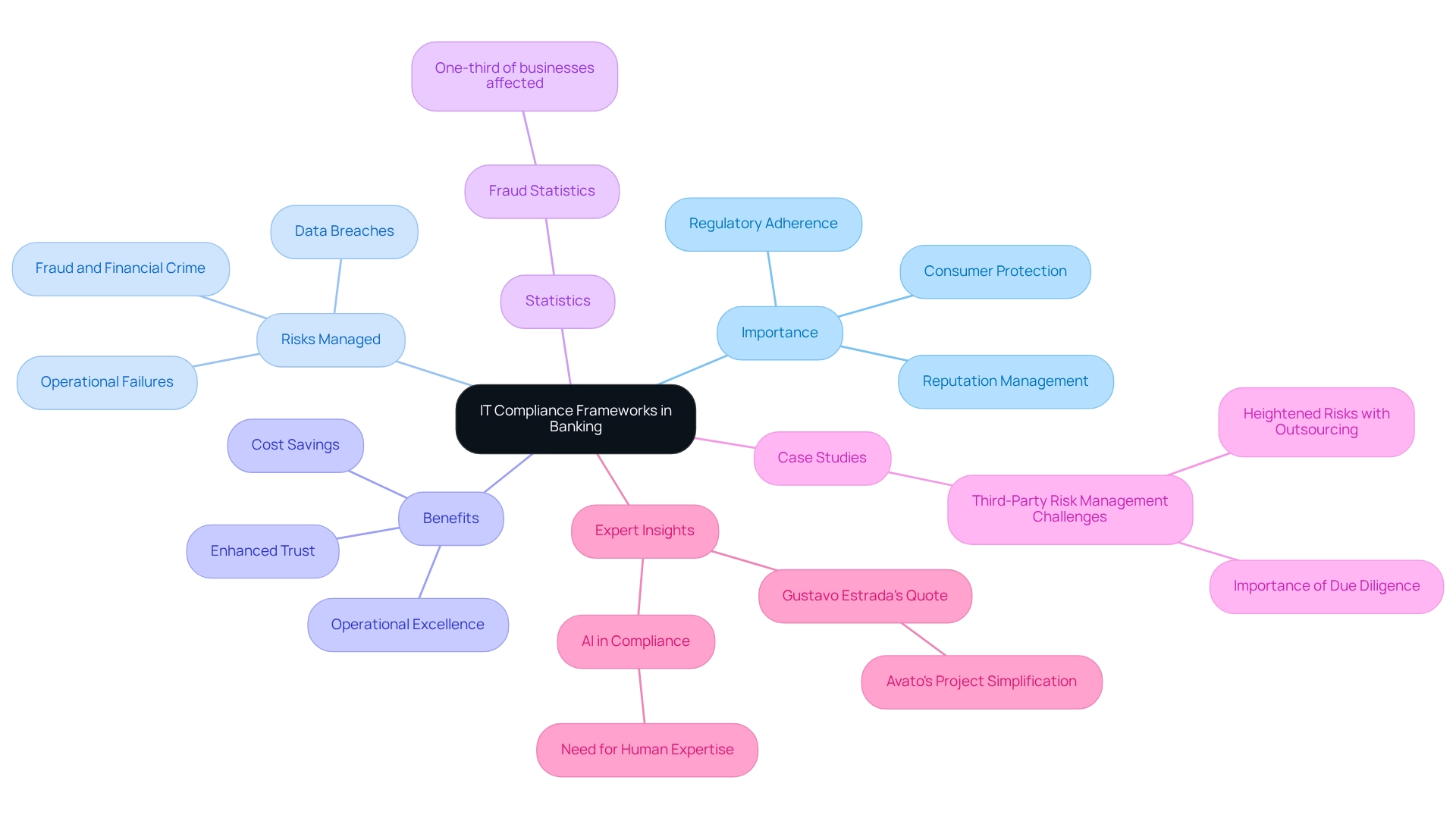
In the banking sector, IT compliance frameworks are crucial for ensuring adherence to regulations that protect consumers and uphold financial stability. These frameworks play a vital role in managing risks associated with financial crimes, data breaches, and operational failures. Alarmingly, statistics reveal that nearly one-third of companies have experienced fraud or financial crime in the past five years, underscoring the urgent need for robust regulatory measures.
Establishing effective IT compliance frameworks not only helps banks avoid costly penalties but also bolsters their reputation with regulators and clients. For instance, organizations prioritizing third-party oversight have reported significant reductions in legal, financial, and reputational challenges, particularly when robust due diligence programs are in place. Despite the complexities of outsourcing tasks to external vendors, many industry professionals assert that continuous monitoring and integrity audits are essential for maintaining trust and integrity.
A case study illustrates that firms with strong vendor risk management practices can substantially mitigate risks linked to third-party relationships.
The financial implications of regulatory frameworks are considerable. By optimizing operations and lowering the chances of breaches, banks can realize significant cost savings. Furthermore, these regulatory structures serve as a safeguard for consumers, ensuring their information is managed securely and responsibly.
As we approach 2025, the importance of these frameworks will only escalate, with banking regulators emphasizing their role in fostering a secure financial environment.
Numerous examples exist of banks that have successfully enhanced their reputation through diligent compliance with regulations. By adopting comprehensive frameworks, these institutions not only meet regulatory requirements but also build trust with their clients, positioning themselves as leaders in the industry. Expert insights consistently highlight that IT compliance frameworks, as a structured regulatory system, are not merely a legal obligation but a strategic advantage that can elevate operational excellence and customer loyalty.
As Gustavo Estrada noted, “Avato has the ability to simplify complex projects and deliver results within desired time frames and budget constraints,” which emphasizes how Avato’s dedicated hybrid integration platform can assist banks in modernizing legacy systems, ensuring seamless and secure data connectivity, and improving operational visibility. By addressing specific regulatory challenges faced by financial IT managers, Avato empowers institutions to enhance their compliance capabilities and ultimately achieve successful project outcomes.
Top 7 IT Compliance Frameworks for Banking
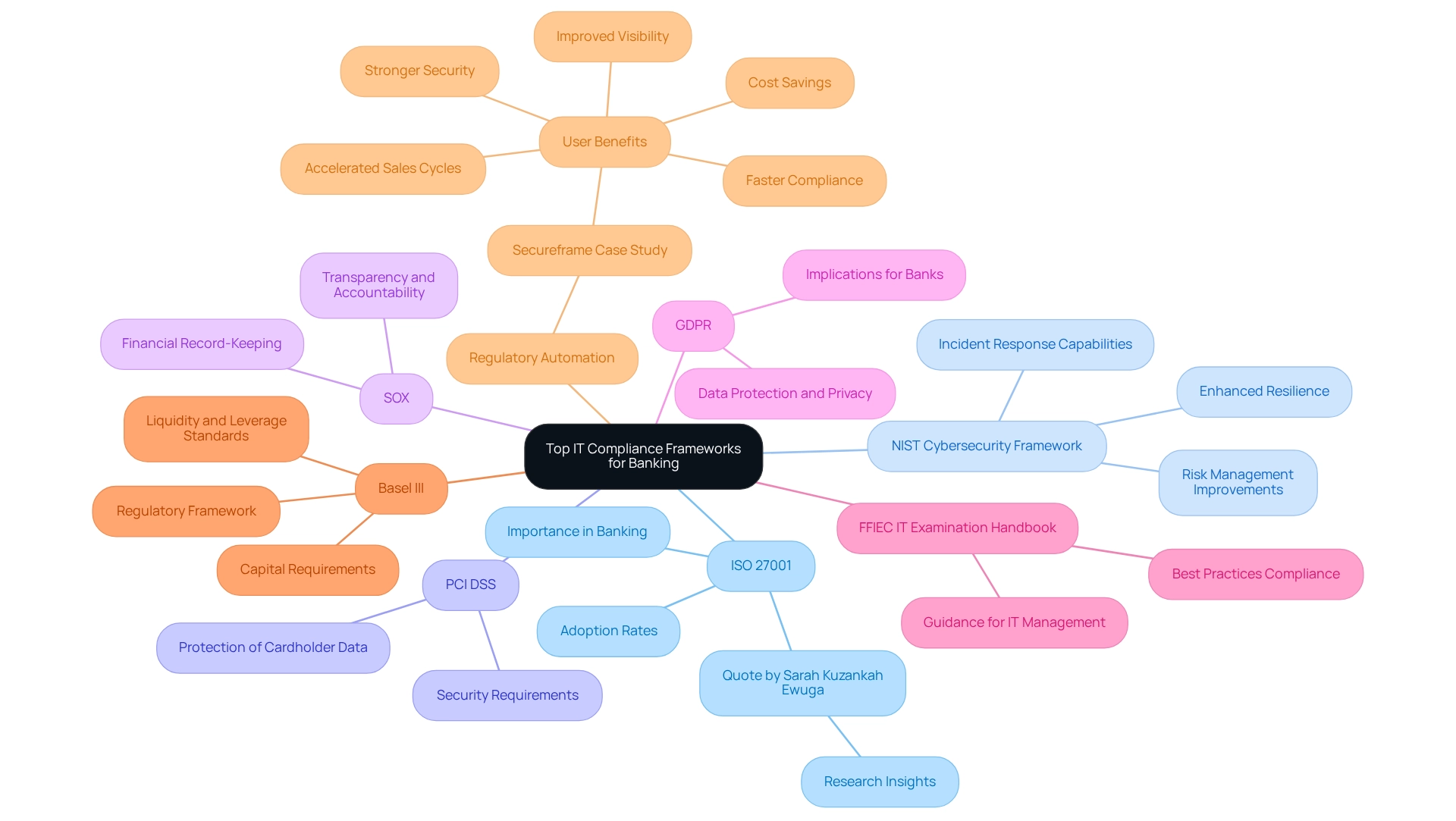
- ISO 27001: This structure is pivotal for establishing an Information Security Management System (ISMS), ensuring that organizations systematically manage sensitive information. This approach not only enhances data security but also integrates compliance frameworks. Current adoption rates indicate a growing recognition of its importance, particularly in the financial sector, where safeguarding customer data is paramount. As independent researcher Sarah Kuzankah Ewuga notes, “This research provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of ISO 27001 as a strategic structure for information security in banking.”
- NIST Cybersecurity Structure: Designed to assist organizations in managing and mitigating cybersecurity risk, this guide offers a structured approach for assessing and improving security posture. Recent statistics reveal that financial institutions adopting the NIST framework have reported significant improvements in their ability to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats. Many institutions cite enhanced resilience in their information security controls. Furthermore, with 67% of global executives finding ESG regulation too complex, the challenges IT managers in the finance sector face with compliance frameworks become evident.
- PCI DSS: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard is essential for any organization that handles credit card transactions. It establishes stringent security requirements to protect cardholder data, ensuring that financial institutions maintain a secure environment against data breaches.
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): This legislation mandates rigorous practices in financial record-keeping and reporting, particularly for publicly traded companies. Adherence to SOX is essential for upholding transparency and accountability in financial reporting, which is crucial for trust in the financial sector.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): As a comprehensive regulation governing data protection and privacy in the EU, GDPR has significant implications for banks operating within or dealing with EU citizens. Compliance not only protects customer data but also enhances the institution’s reputation and trustworthiness.
- FFIEC IT Examination Handbook: This handbook offers crucial guidance for financial institutions on IT management, ensuring that banks comply with best practices in technology governance and security. It serves as a critical resource for compliance officers and IT managers working within compliance frameworks in the financial sector.
- Basel III: This global regulatory framework aims to strengthen regulation, supervision, and risk management within the financial sector. By establishing more stringent capital requirements and introducing new regulatory standards on liquidity and leverage, Basel III enhances the resilience of financial institutions and systems, ensuring they can withstand financial shocks.
- Regulatory Automation: A case study on Secureframe highlights the advantages of regulatory automation, revealing that 97% of users reported stronger security, and 89% experienced faster adherence. This underscores the importance of incorporating regulatory structures into financial operations.
Key Features of Effective IT Compliance Frameworks
Efficient IT compliance frameworks are crucial for financial institutions to navigate the complexities of regulatory obligations and mitigate risks. The following essential characteristics are vital to these frameworks:
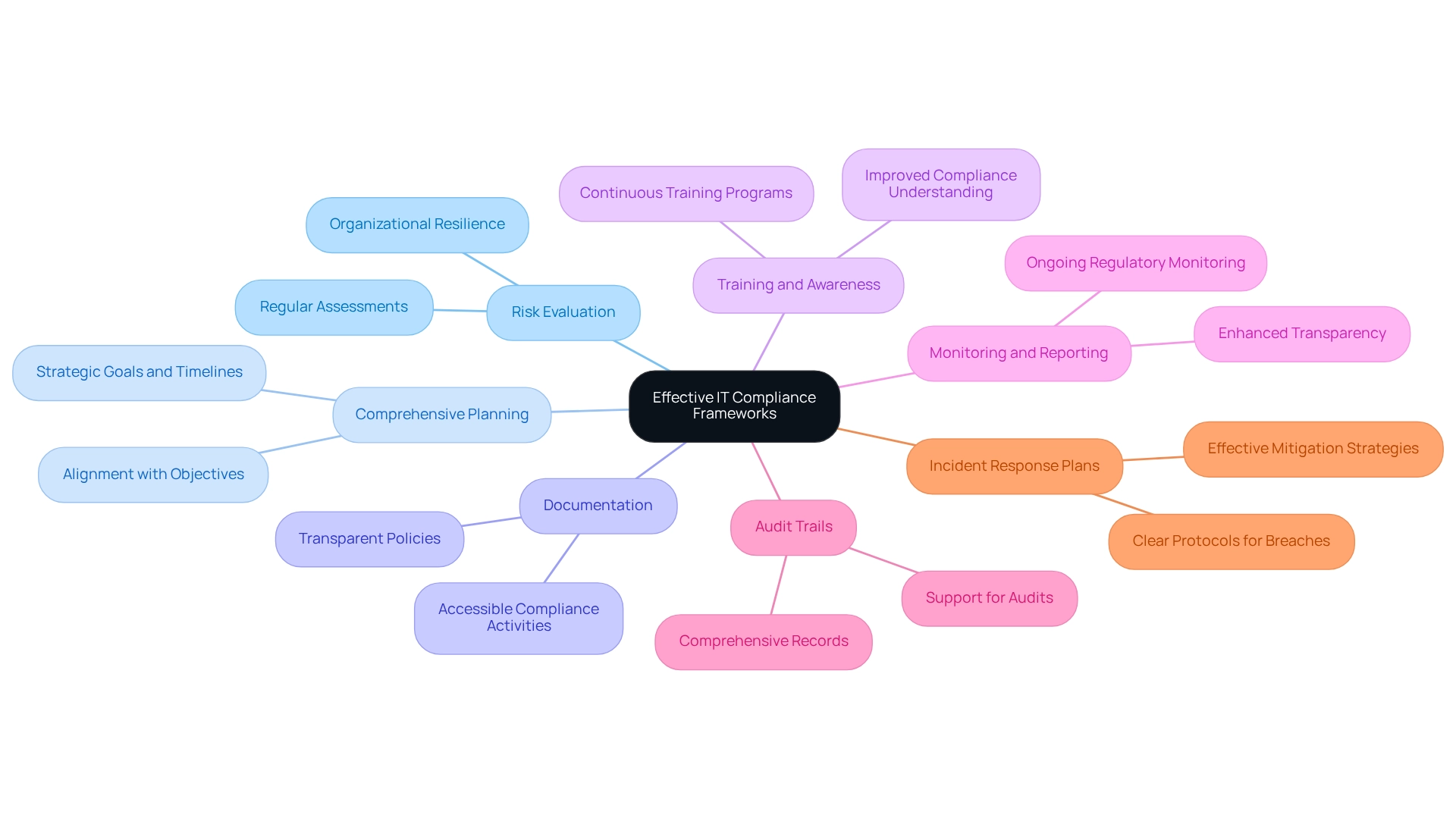
- Risk Evaluation: Regular assessments are critical for identifying and mitigating compliance threats. This proactive approach not only aids in adhering to regulations but also bolsters overall organizational resilience. Notably, statistics reveal that the top 10% of organizations are five times more likely to express confidence in achieving their risk management goals, highlighting the importance of robust risk assessment practices in the banking sector. By leveraging Avato’s Hybrid Integration Platform, institutions can conduct thorough evaluations of their current systems, pinpointing areas that would benefit most from modernization.
- Comprehensive Planning: Crafting a comprehensive plan that aligns with your institution’s objectives is imperative. This plan should delineate specific goals, methodologies, and timelines for modernization efforts, ensuring that all compliance initiatives are strategically aligned with the institution’s mission and regulatory requirements.
- Documentation: Meticulous documentation of policies, procedures, and compliance activities is essential. Effective documentation practices ensure that all compliance efforts are transparent and readily accessible, facilitating smoother audits and reviews.
- Training and Awareness: Continuous training programs are necessary to ensure that all employees grasp regulatory requirements. Statistics indicate that organizations with structured training programs experience a significant improvement in compliance, as employees are better equipped to identify and address regulatory issues.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Implementing tools for ongoing monitoring of regulatory status is crucial. These tools provide immediate insights and reporting systems that enhance transparency and accountability within the organization.
- Audit Trails: Maintaining comprehensive records of regulatory activities is vital for supporting audits and reviews. A well-documented audit trail not only assists in compliance initiatives but also fosters trust with stakeholders.
- Incident Response Plans: Establishing clear protocols for addressing breaches or failures in regulations is essential. These strategies ensure that entities can respond promptly and effectively to mitigate the impacts of any regulatory incidents.
Integrating these elements into IT compliance frameworks not only strengthens an organization’s regulatory posture but also aligns with the growing emphasis on addressing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) matters. Furthermore, leveraging reliable technology stacks, such as those provided by Avato, can significantly assist businesses in adapting to these evolving demands and maintaining a competitive advantage.
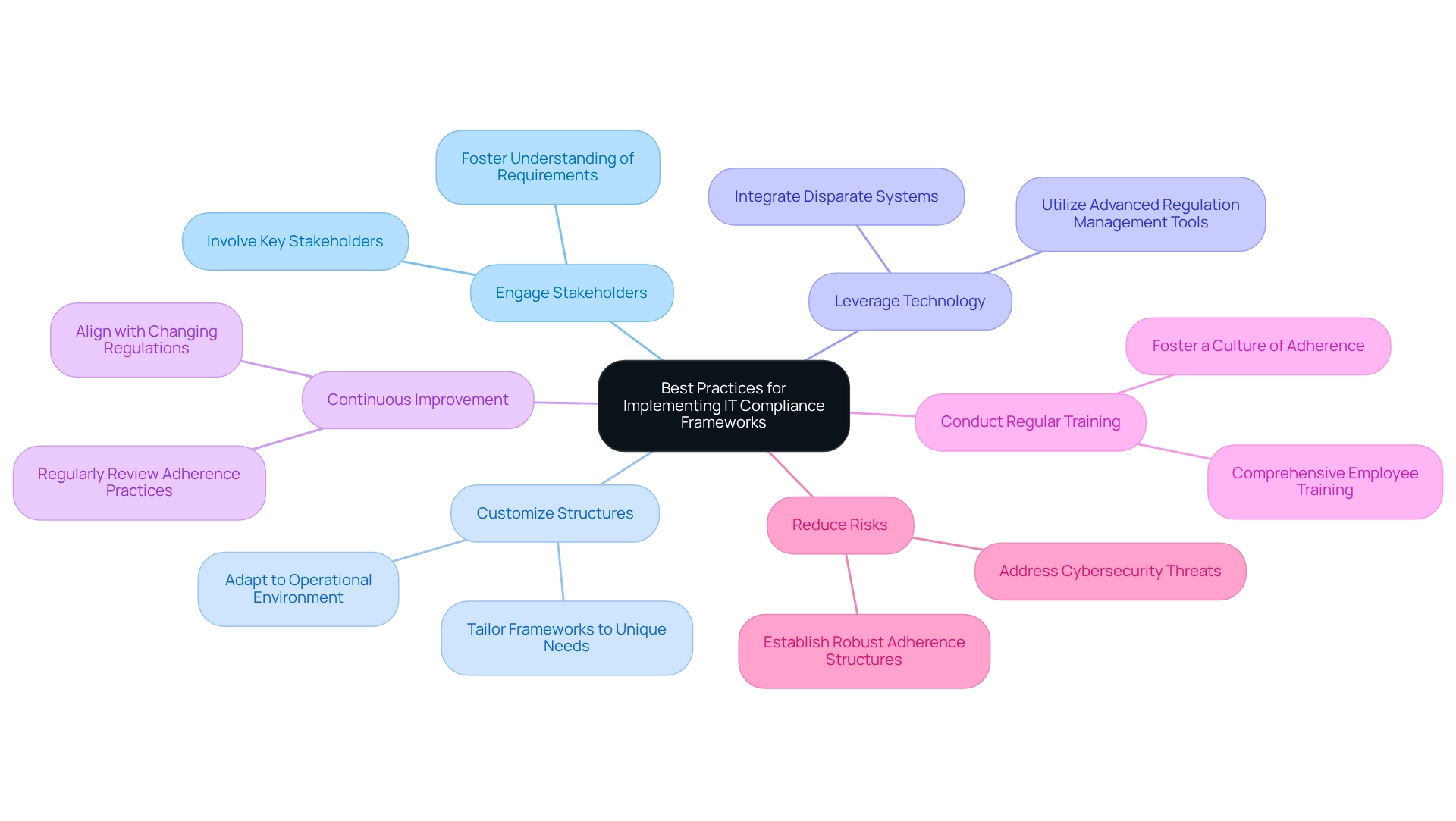
Implementing IT Compliance Frameworks: Best Practices
To effectively implement IT adherence structures, banking IT managers must embrace several best practices:
-
Engage Stakeholders: Are you actively involving key stakeholders from safety management, legal, and operations? By fostering a comprehensive understanding of adherence requirements, you can ensure broad support across the organization. This collaborative approach significantly enhances stakeholder involvement success rates in regulatory initiatives.
-
Customize Structures: Is your regulatory framework tailored to meet the unique requirements and risks of your organization? A one-size-fits-all approach often falls short; thus, adapting compliance frameworks to fit the specific operational environment of the bank is crucial for effective regulation management.
-
Leverage Technology: Have you considered utilizing advanced regulation management tools and software, such as those offered by Avato? These solutions streamline processes, enhance monitoring capabilities, and ensure real-time tracking. Avato’s dedicated hybrid integration platform simplifies the integration of disparate systems, enabling organizations to efficiently adapt to evolving regulatory demands. This technology not only simplifies regulatory tasks but also enhances overall business value by unlocking isolated assets. Avato’s commitment to designing the technological groundwork necessary for rich, connected customer experiences is vital in this process.
-
Continuous Improvement: Are you regularly reviewing and updating your adherence practices? Staying aligned with changing regulations and organizational needs is essential. This proactive approach is critical in a landscape where 67% of global executives find compliance frameworks related to ESG regulation too complex. As Gustavo Estrada noted, Avato streamlines intricate projects, delivering outcomes within preferred timelines and financial limits, which is essential for sustaining effective adherence.
-
Conduct Regular Training: Are all employees receiving comprehensive training on adherence policies and procedures? Fostering a culture of adherence through ongoing education is vital for upholding regulations and minimizing risks associated with non-conformity.
-
Reduce Risks: With cyberattacks targeting third parties increasing from 44% to 49% over the past year, establishing robust adherence structures is imperative. These structures must efficiently address these threats and protect the organization.
By implementing these best practices, banking IT managers can enhance their adherence systems, ensuring they are not only effective but also resilient in the face of evolving regulatory challenges.
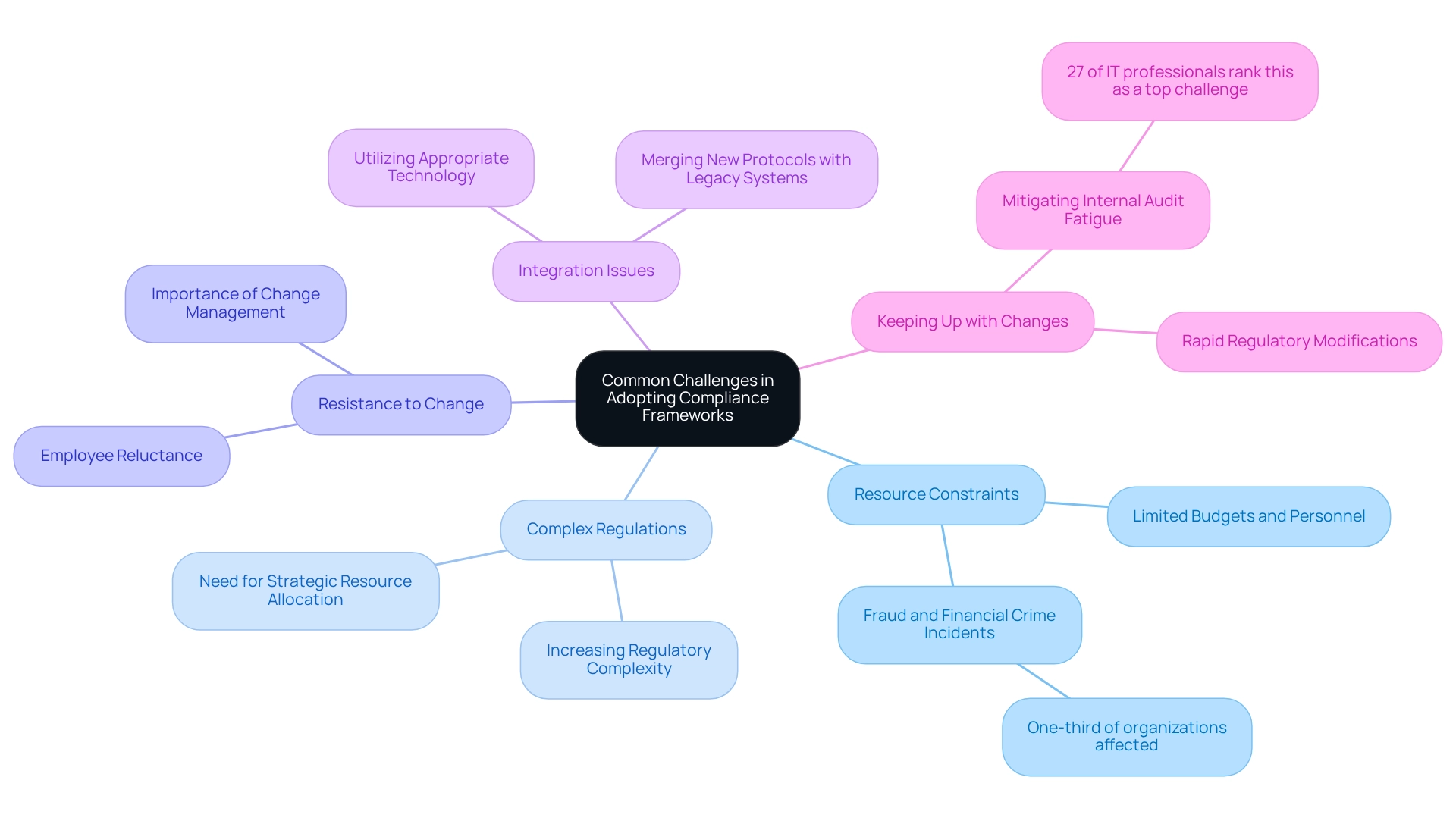
Common Challenges in Adopting Compliance Frameworks
Banking IT leaders frequently encounter a myriad of challenges when establishing compliance frameworks, significantly impacting their organizations’ ability to meet regulatory requirements efficiently. Key obstacles include:
- Resource Constraints: Limited budgets and personnel often impede adherence initiatives. A substantial number of organizations report that nearly one-third have experienced fraud or financial crime in the past five years. This statistic underscores the urgent need for robust regulatory measures, even amid resource limitations. IT managers in the financial sector must prioritize adherence, regardless of resource constraints.
- Complex Regulations: The regulatory landscape is increasingly intricate, posing significant navigation challenges for financial institutions. As regulations evolve, the complexity can overwhelm oversight teams, necessitating a strategic approach to resource allocation. The regulatory landscape for 2024 is marked by ongoing changes, requiring banking IT managers to stay ahead to ensure compliance.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new regulatory processes, hindering implementation efforts. This resistance often arises from a lack of understanding or fear of increased workloads, making effective change management crucial. Engaging stakeholders to accurately capture requirements from the outset is vital in overcoming this challenge.
- Integration Issues: Merging regulatory frameworks with existing systems presents a considerable challenge. Many banks struggle to align new regulatory protocols with legacy systems, leading to inefficiencies and potential compliance gaps. Utilizing appropriate technology and tools to accurately represent the current situation and desired outcomes can help mitigate these integration difficulties.
- Keeping Up with Changes: The rapid pace of regulatory modifications complicates adherence efforts. In 2024, the regulatory environment is characterized by continuous change, necessitating proactive management to ensure compliance with new rules. Moreover, a recent study reveals that 27% of security and IT professionals identify alleviating internal audit fatigue as a primary challenge, highlighting the need for streamlined processes. Successful banks demonstrate resilience in managing these complexities; for instance, 91% of business leaders acknowledge the importance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) compliance, reflecting a growing commitment to responsible practices. This trend illustrates how banks can leverage compliance frameworks to effectively navigate broader regulatory challenges through ESG adherence.
Expert opinions affirm that addressing these challenges is essential for sustaining compliance frameworks and operational efficiency. As Ayush Saxena notes, appointing a C-level regulatory leader can yield significant cost reductions, averaging $1.25 million. This observation highlights the financial benefits of prioritizing leadership in resource allocation strategies, as such leadership can optimize regulatory processes and address the challenges faced by IT managers in the financial sector.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, IT managers in the financial sector can enhance their organizations’ ability to thrive in a complex regulatory environment.
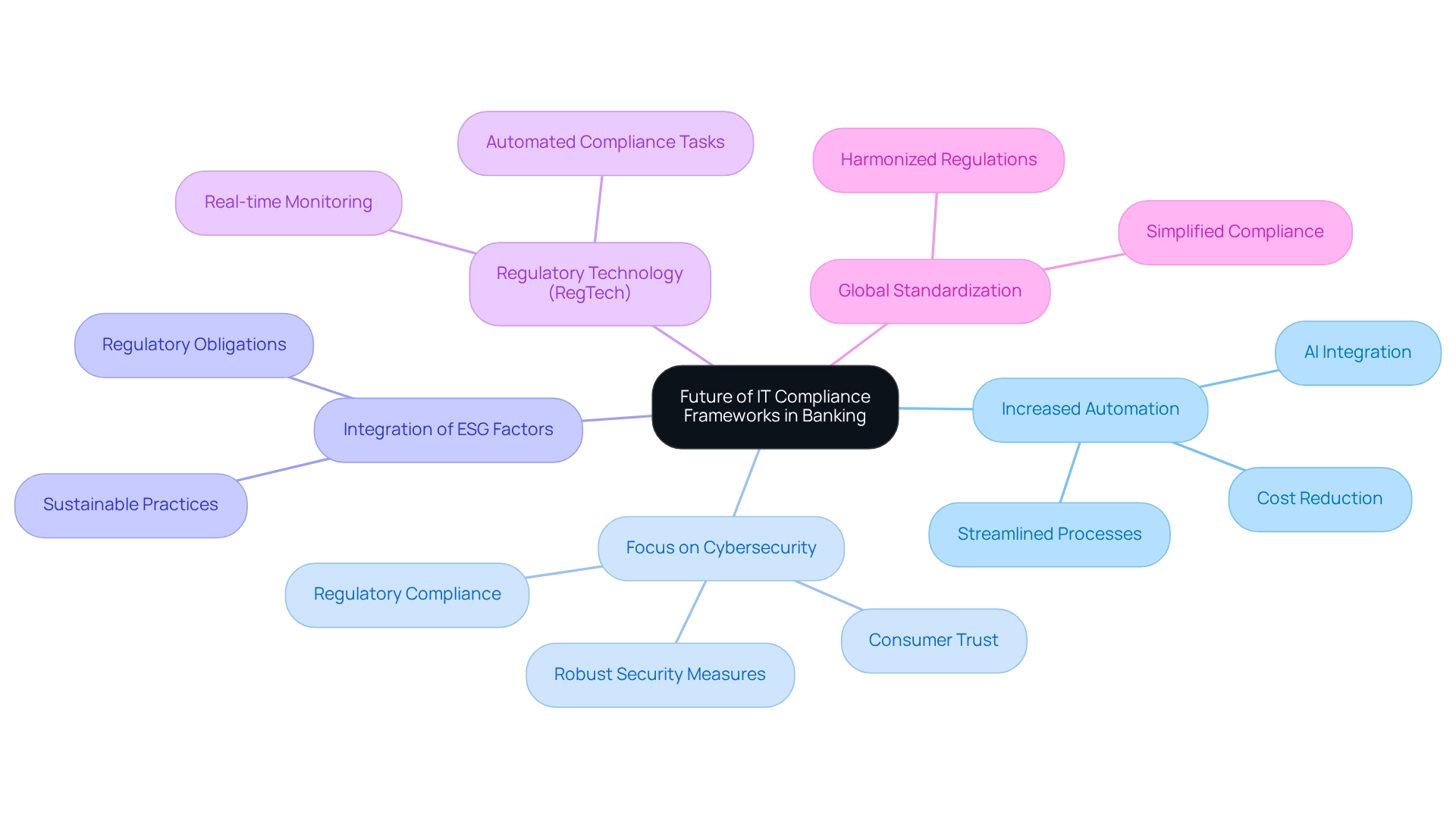
The Future of IT Compliance Frameworks in Banking
As the banking sector continues to evolve, compliance frameworks must adapt to meet new challenges and seize opportunities. Key trends shaping the future of compliance frameworks include:
- Increased Automation: The integration of AI and machine learning is revolutionizing compliance processes, significantly reducing manual efforts and enhancing accuracy. Automation streamlines workflows and mitigates regulatory risks, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to regulatory changes. Avato’s Secure Hybrid Integration Platform exemplifies this trend by maximizing the value of legacy systems, simplifying complex integrations, and significantly lowering costs. As Sharavanan, Associate Product Marketing Manager, observes, “These trends underscore the dynamic nature of the regulatory environment, emphasizing the significance of remaining informed and proactive in managing requirements.”
- Focus on Cybersecurity: As cyber threats grow increasingly sophisticated, there is a heightened emphasis on cybersecurity standards. Banks are prioritizing robust security measures to protect sensitive data and maintain customer trust, recognizing that 76% of consumers would cease support for companies perceived as neglecting their responsibilities to employees and communities. This statistic underscores the essential role that regulatory structures play in safeguarding customer relationships.
- Integration of ESG Factors: Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations are gaining traction within regulatory frameworks. Financial organizations are progressively obliged to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices, making ESG integration a crucial component of regulatory strategies.
- Regulatory Technology (RegTech): The adoption of innovative technologies, known as RegTech, is enhancing adherence monitoring and reporting capabilities. These tools empower banks to automate regulatory tasks, ensuring compliance with legal requirements while boosting efficiency. Avato’s platform facilitates this by providing real-time tracking and notifications on system performance, further improving regulatory management.
- Global Standardization: A growing movement towards harmonizing regulatory standards across jurisdictions aims to simplify compliance for multinational banks, enabling more effective operations in diverse regulatory environments.
A significant case study highlights the transformative impact of automation in regulatory management for financial institutions. A prominent power and utility firm faced major challenges in managing Change-in-Law adherence due to a manual tracking process that was both time-consuming and error-prone. By implementing Agentic Process Automation, which utilized three AI-powered agents, the organization improved its regulatory management process.
This automation not only eliminated inefficiencies but also reduced regulatory risks and enhanced response times, allowing the company to maintain standards without the burden of manual oversight. Similar challenges are faced by banks, where manual processes can lead to increased risks and inefficiencies in regulatory management. Leveraging Avato’s Hybrid Integration Platform can accelerate the integration of isolated legacy systems, ensuring 24/7 uptime and reliability for complex systems in finance, healthcare, and government while significantly lowering costs.
As we look towards 2025, the future of compliance frameworks in banking will likely be characterized by these trends, with automation playing a pivotal role in enhancing compliance processes and ensuring that institutions can effectively navigate the complexities of regulatory landscapes.
Conclusion
The significance of IT compliance frameworks in banking is paramount. These frameworks act as essential tools for navigating a complex regulatory landscape while safeguarding sensitive data. By adopting structured guidelines such as ISO standards and NIST frameworks, banking institutions can effectively mitigate risks associated with data breaches and financial crimes, thereby enhancing their operational resilience.
The increasing specialization in compliance roles underscores the necessity for IT managers to remain informed and adaptable in the face of evolving regulations. The statistics presented reveal a pressing need for organizations to prioritize compliance frameworks, highlighting the potential for substantial cost savings and reputational benefits. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of advanced technologies alongside a focus on cybersecurity will further reinforce the importance of these frameworks.
As the banking sector advances towards 2025, the emphasis on effective IT compliance frameworks will intensify. By implementing best practices, leveraging technology, and fostering a culture of compliance, banking IT managers can position their organizations not just to meet regulatory demands but to excel in a competitive landscape. The proactive adoption of these frameworks transcends mere regulatory necessity; it represents a strategic advantage that can drive operational excellence and cultivate enduring trust with customers.

