Overview
This article delves into the critical role of FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) interoperability in enhancing healthcare information exchange. FHIR is not just a technical standard; it is essential for improving the accessibility and coordination of medical data across diverse systems. This capability is crucial for delivering high-quality patient care.
As the adoption of FHIR grows, so does the need for standardized frameworks to tackle existing interoperability challenges in healthcare. How can we ensure that all healthcare systems communicate effectively? The integration of FHIR offers a promising solution, paving the way for a more cohesive healthcare landscape.
By embracing FHIR, we can overcome barriers to information exchange, ultimately benefiting patients and providers alike. The time to act is now—prioritizing FHIR interoperability is imperative for the future of healthcare.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare, the need for seamless data exchange is more critical than ever. Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) emerges as a transformative solution, designed to bridge the gaps between disparate healthcare systems and enhance interoperability. By addressing the challenges of fragmented data, FHIR not only facilitates efficient access to patient information but also paves the way for innovative applications that can revolutionize patient care.
As healthcare organizations increasingly recognize the potential of FHIR to streamline operations and improve outcomes, understanding its architecture, real-world applications, and implementation best practices becomes essential. This exploration delves into the significance of FHIR, its evolution from previous standards, and the future trends that promise to redefine healthcare interoperability.
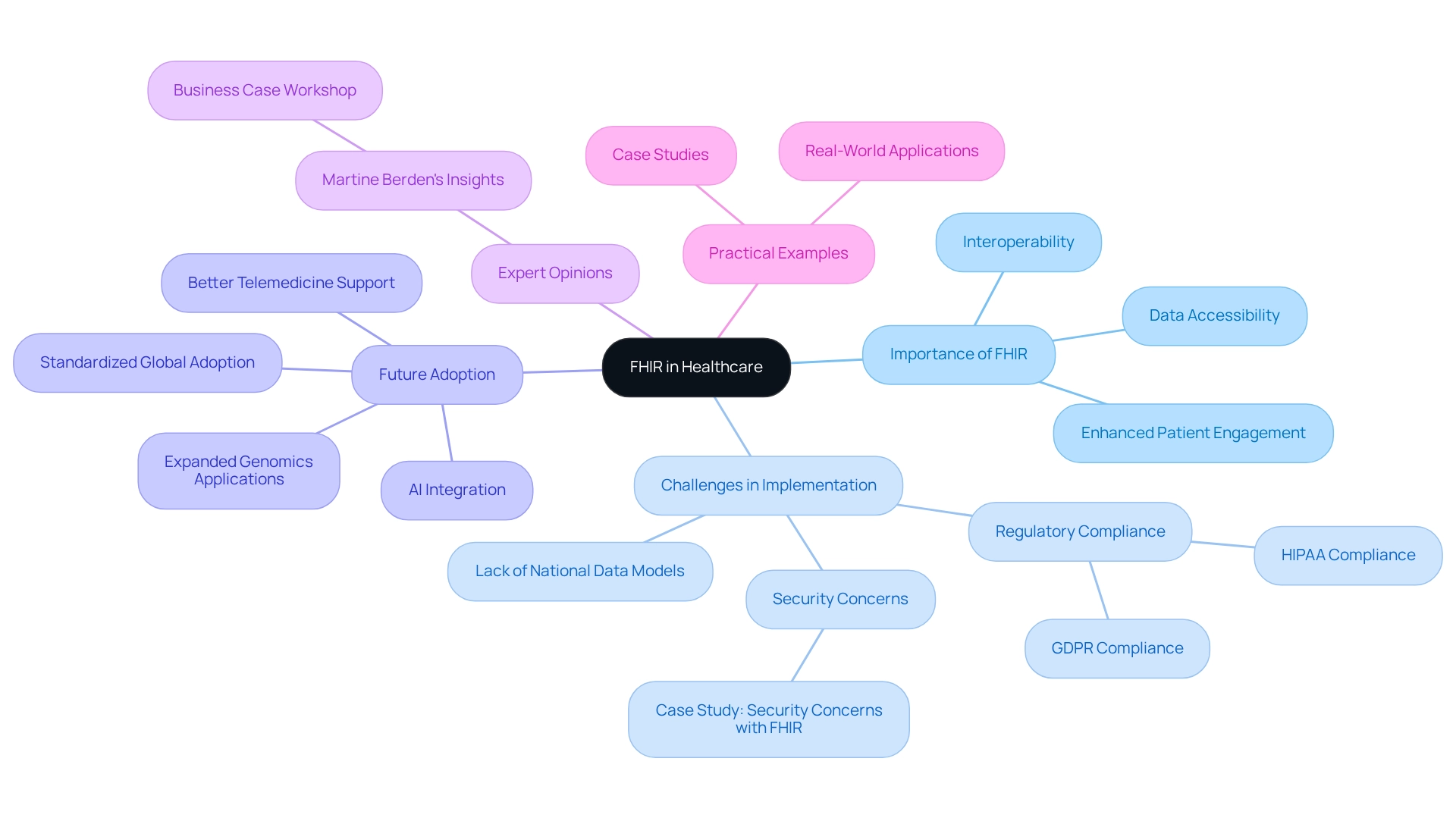
What is FHIR and Why is It Important for Healthcare?
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources, or FHIR, is a crucial standard for the electronic exchange of medical information that specifically enhances FHIR interoperability among various health systems. By tackling the widespread problem of disjointed health information, this standard empowers medical professionals to effectively retrieve and distribute patient details, which is essential for providing top-notch care.
The importance of this standard extends beyond simple information exchange; it is critical in enhancing health system FHIR interoperability. Current statistics reveal that while over 80% of nations have regulations mandating the use of standards for electronic health information exchange, a national framework based on those standards remains absent in many areas. This gap underscores the urgent need for standardized frameworks to facilitate seamless communication across medical platforms.
Significantly, six participants from five nations indicated that a national data model does not yet exist, highlighting the challenges faced in achieving complete interoperability.
Moreover, the adoption of this standard is on the rise, with numerous medical organizations recognizing its potential to enhance operations through FHIR interoperability. By 2025, an increasing number of medical systems are expected to incorporate interoperability standards, driven by the capability to support diverse applications, from electronic health records (EHRs) to mobile health solutions. This integration not only improves patient care but also boosts operational efficiency, enabling providers to respond more swiftly to patient needs.
Avato’s dedicated hybrid integration platform, which supports 12 levels of interface maturity, offers a structured approach to health data integration, accommodating varying levels of complexity in medical systems and empowering businesses to future-proof their operations through seamless data and system integration.
Expert opinions highlight the transformative benefits of health data standards in medical interoperability. For instance, Martine Berden emphasized the significance of a business case workshop for successful implementation. Additionally, the execution of the standard must prioritize adherence to privacy regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, addressing security issues that are crucial for effective integration.
Practical instances illustrate how this standard has enhanced interoperability, allowing medical providers to deliver coordinated care and improved outcomes for individuals. A case study on security concerns with FHIR demonstrates that addressing compliance issues is essential for the successful and secure implementation of the standard in the medical domain.
In summary, this standard is not merely a technical guideline; it is a vital element in advancing medical FHIR interoperability. Its benefits encompass improved data accessibility, enhanced patient engagement, and the potential for innovative applications such as AI integration and expanded genomics capabilities. As the medical landscape continues to evolve, this standard stands out as a cornerstone for achieving a more connected and efficient medical system, with Avato leading the way in providing the necessary integration solutions.
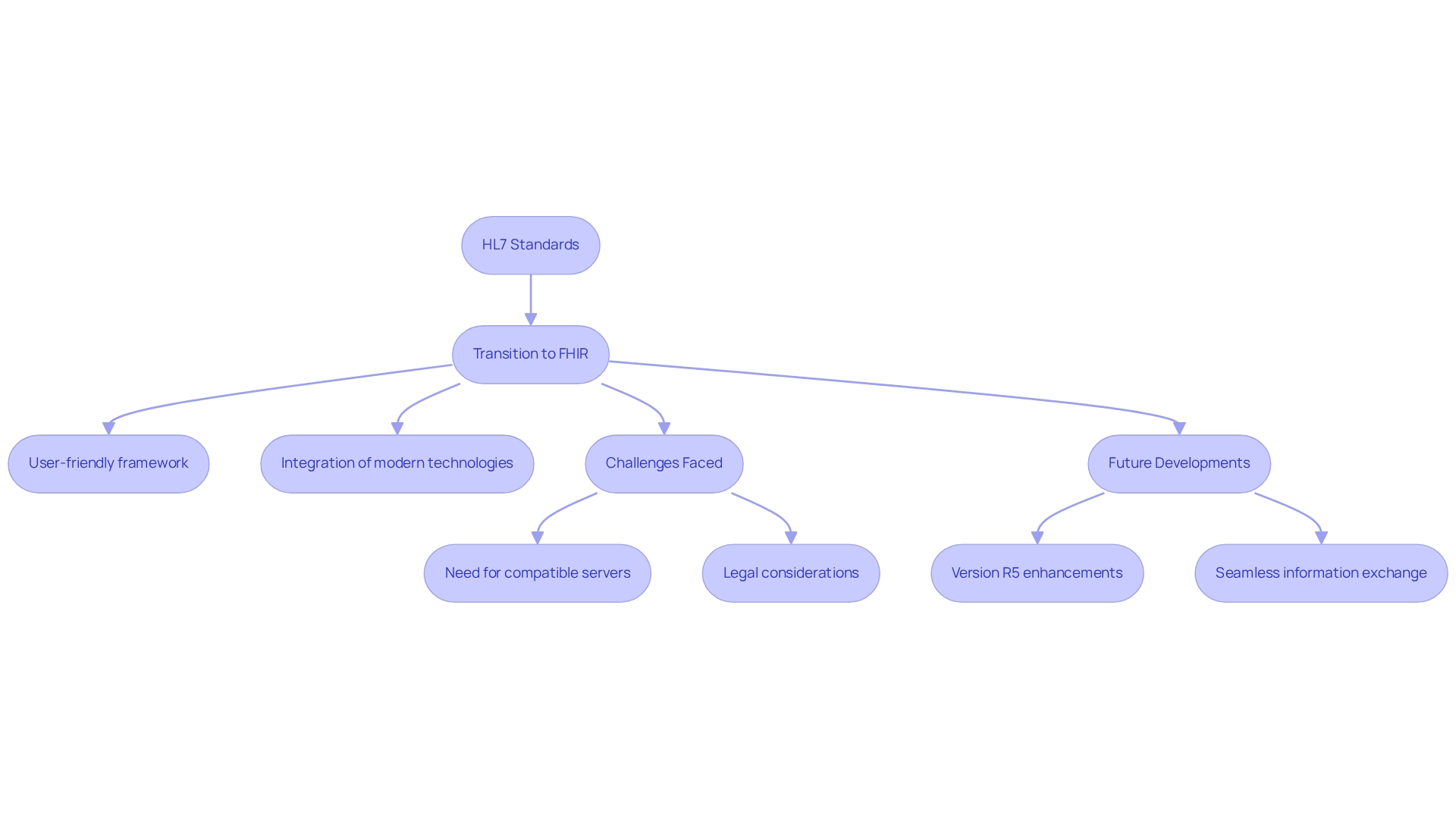
The Evolution of FHIR: From HL7 to Modern Interoperability Standards
The standard has significantly advanced from its predecessors, particularly HL7 v2 and v3, which faced frequent criticism for their complexity and implementation challenges. Launched in 2011, this evolution aimed to establish a more adaptable and user-friendly framework that effectively addresses the requirements of contemporary medical systems. By integrating modern web technologies such as RESTful APIs, JSON, and XML, this standard not only streamlines information exchange but also enhances FHIR interoperability across diverse medical platforms.
This evolution reflects a broader shift within the healthcare sector towards agile and flexible solutions for information sharing. Recent statistics indicate that 18% of studies have utilized standardized terminologies like LOINC, SNOMED CT, or ICD-10, underscoring the growing significance of FHIR interoperability in health research. Moreover, the transition from HL7 to a newer standard has been characterized by notable developments, including the identification of essential information for transforming data based on this standard into case report forms, which aims to advance the HL7 standard for multi-site clinical research data collection.
Organizations transitioning from HL7 to the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources standard have encountered various challenges, including the need for compatible servers and legal considerations surrounding electronic consents. As emphasized in the case study titled ‘Challenges and Limitations of FHIR Interoperability,’ these complexities highlight the ongoing necessity for research and development to address the constraints associated with the implementation of FHIR interoperability. Umit Topaloglu, PhD, asserts that ‘the development of this standard signifies an essential move towards achieving FHIR interoperability in medical systems.’
Furthermore, anticipated changes in version R5 are expected to enhance FHIR interoperability in health research, further facilitating seamless information exchange among medical providers. As the medical landscape continues to evolve, the implementation of standards is projected to be crucial in improving FHIR interoperability and enabling smooth data exchange among medical providers. John Johnstone notes that Avato streamlines intricate projects, delivering outcomes within preferred time limits and financial constraints, which can be particularly advantageous for organizations grappling with the challenges of implementation.
Avato’s Hybrid Integration Platform maximizes the value of legacy systems, simplifies complex integrations, and significantly reduces costs, ensuring 24/7 uptime and reliability for intricate systems in banking, medical services, and government. Additionally, the platform provides real-time monitoring and alerts on system performance, further enhancing its effectiveness in managing integrations.
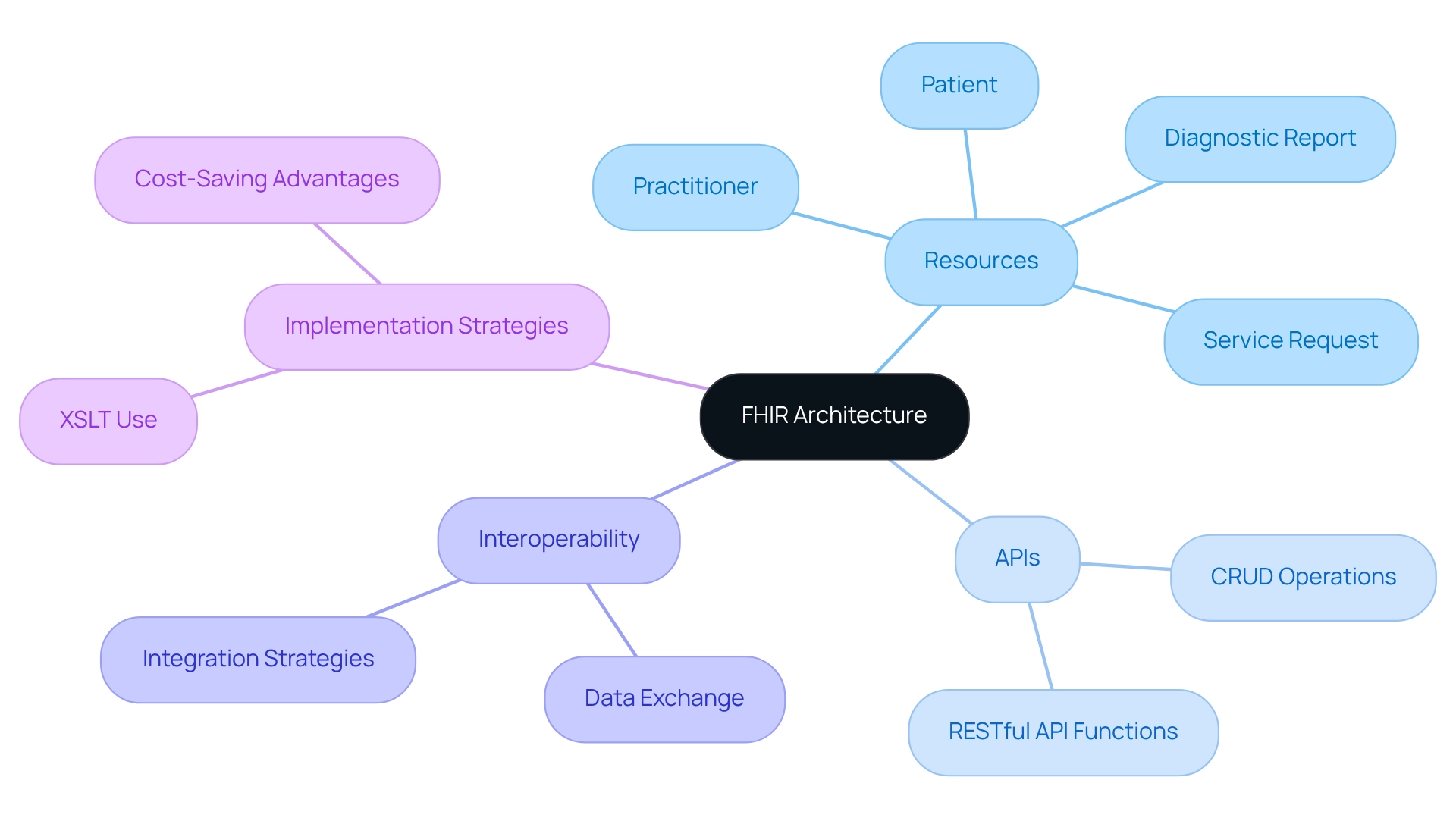
Understanding FHIR Architecture: Resources, APIs, and Data Exchange
The architecture of the standard is fundamentally organized around resources, which serve as the essential building blocks. Each resource encompasses a specific category of medical information, such as patient details, medications, or clinical observations. This modular approach not only streamlines information management but also enhances FHIR interoperability across various medical systems, aligning seamlessly with Avato’s Hybrid Integration Platform’s objective of successful digital transformation.
At the core of FHIR’s functionality are RESTful APIs, facilitating efficient information exchange between systems. These APIs enable a variety of operations, including create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) actions, ensuring that medical applications can integrate seamlessly with one another. This capability is essential for contemporary medical settings, where prompt access to precise information can significantly influence patient outcomes.
Grasping the complexities of health information architecture is crucial for successful execution. For instance, a case study analyzing historical medical test order patterns demonstrated how information obtained from health resources—such as Patient, Practitioner, DiagnosticReport, and ServiceRequest—can provide valuable insights into medical practices over time. This analysis not only highlights the versatility of health information resources but also underscores their potential in identifying trends and enhancing clinical decision-making.
Significantly, the analysis of clinical information can assist in recognizing possible biomarkers for illness diagnosis and prognosis, further emphasizing the importance of standardized data exchange protocols in medical environments. Furthermore, recent statistics indicate that the utilization of RESTful APIs in medical integration is on the rise, with numerous organizations leveraging these technologies to enhance their information exchange capabilities. An intuitive user interface designed for information analysis showcases the practical utility of the standard, enabling end-users to access and examine information effectively.
As healthcare systems increasingly prioritize FHIR interoperability, mastering the architecture and its elements will be vital for professionals seeking to enhance their integration strategies and elevate patient care.
In this context, employing XSLT for efficient XML transformation can significantly reduce programming errors and labor costs associated with integration projects. The cost-saving advantages of schemas in information management further enhance the value of healthcare integration, ensuring information longevity and FHIR interoperability. As Carina Nina Vorisek observed, adhering to established guidelines such as PRISMA in research bolsters the credibility of studies related to health information exchange analysis, underscoring the necessity for rigorous methodologies in this evolving field.
For banking IT managers, understanding how this integration can impact the financial aspects of health systems and the significance of secure information exchange in financial transactions tied to health is essential.
To further facilitate effective digital transformation, consulting the infographic detailing the five essential steps in this process is advantageous. Moreover, practical guidance on implementing standards and XSLT within Avato’s Hybrid Integration Platform can provide valuable insights for banking IT managers aiming to enhance their integration strategies.
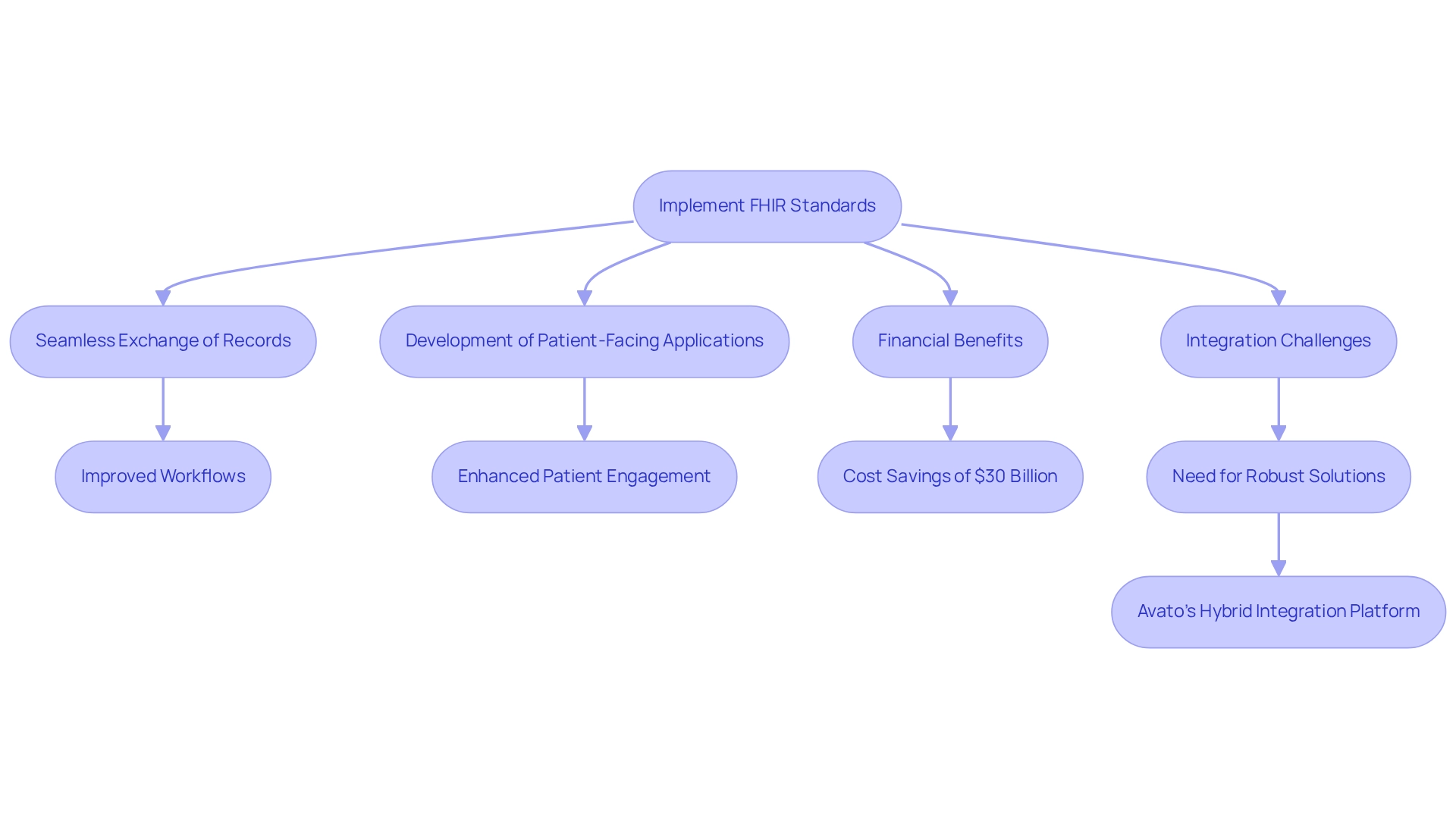
Real-World Applications of FHIR: Enhancing Patient Care and Data Management
In practical applications, this standard significantly enhances individual care and streamlines medical data management. Medical providers leverage standardized protocols to facilitate the seamless exchange of client records across diverse systems, ensuring clinicians have immediate access to comprehensive and current information. This capability not only improves workflows but also reduces the risk of errors associated with incomplete data.
Furthermore, this standard fosters the development of innovative patient-facing applications that empower individuals to engage actively in their health journey. These applications enable users to access their health information, schedule appointments, and communicate directly with their medical providers, thereby nurturing a more collaborative health environment. The impact of such tools on client engagement metrics is profound; research indicates that healthcare systems could save up to $30 billion annually by implementing these standards, underscoring their financial and operational benefits.
Practical examples illustrate the effectiveness of these standards in enhancing client care. For instance, medical organizations report improved outcomes for patients through applications that utilize FHIR interoperability to provide timely access to critical health information. Moreover, industry professionals highlight how this framework simplifies health information management while enhancing the overall user experience by making health data more accessible and actionable.
As Gustavo Estrada, a client, noted, Avato streamlines complex projects and delivers results within expected timelines and budget constraints, showcasing the importance of efficient integration in harnessing this system’s capabilities. Avato’s hybrid integration platform is engineered to expedite secure system integration across banking, medical, and government sectors, addressing the challenges posed by isolated legacy systems and fragmented data. As we approach 2025, the ongoing evolution of healthcare applications in care delivery is expected to yield even greater advancements.
Case studies reveal that medical environments utilizing Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources have experienced notable improvements in both patient engagement and care coordination, demonstrating the platform’s critical role in contemporary FHIR interoperability.
Nevertheless, challenges remain within the industry. Epic’s early implementations faced difficulties exporting Bulk Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources for groups of 1,000 patients or more, with some exports taking nearly two weeks to complete. This context highlights the necessity of robust integration solutions like Avato’s hybrid integration platform, which effectively addresses these challenges and enhances the discourse surrounding FHIR interoperability in healthcare settings.
Navigating Challenges: Security and Privacy Concerns in FHIR Interoperability
While FHIR interoperability presents transformative advantages for medical information exchange, it simultaneously introduces significant security and privacy challenges that organizations must confront. Safeguarding individual data during both transmission and storage is paramount. To achieve this, healthcare entities should implement robust authentication and authorization mechanisms, such as OAuth 2.0, which are vital for protecting sensitive information against unauthorized access.
Compliance with regulations like HIPAA transcends mere legal obligation; it is a critical component of maintaining patient trust. Current compliance rates with HIPAA in FHIR implementations reveal that many organizations continue to struggle to meet these standards, underscoring the urgent need for enhanced security measures.
Statistics highlight the necessity of addressing these challenges:
- In 2024, a staggering 100 million individuals were impacted by a breach involving Change Healthcare, Inc., illustrating the vulnerabilities inherent in medical information exchange.
- Furthermore, the average cost of a security breach in the healthcare sector has consistently risen, with a 5.14% increase noted in 2019, emphasizing the financial repercussions of inadequate protection.
Healthcare organizations are increasingly adopting security measures to safeguard FHIR interoperability. For example, Ascension Health’s recent ransomware attack, which affected over 5.5 million individuals, serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of security lapses. As Steve Alder noted, “Some individuals are not anticipated to obtain notification letters until January 2025, 8 months after their information was stolen,” highlighting the damaging effects of security breaches on trust and communication.
Experts emphasize that organizations must prioritize security challenges associated with healthcare FHIR interoperability, especially as the landscape evolves in 2025.
Optimal methods for protecting individual information in these implementations include:
- Conducting regular security evaluations
- Utilizing encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Ensuring that all staff are trained in privacy protocols
Additionally, a case study on the cost estimation of medical data breaches indicates that the average expense of a data breach in the medical field is significantly higher than in other sectors, reinforcing the urgency of implementing effective security measures. By proactively addressing these security issues, medical organizations can foster successful data exchange implementation while preserving the confidence of those they serve.
The Future of FHIR: Trends and Innovations in Healthcare Interoperability
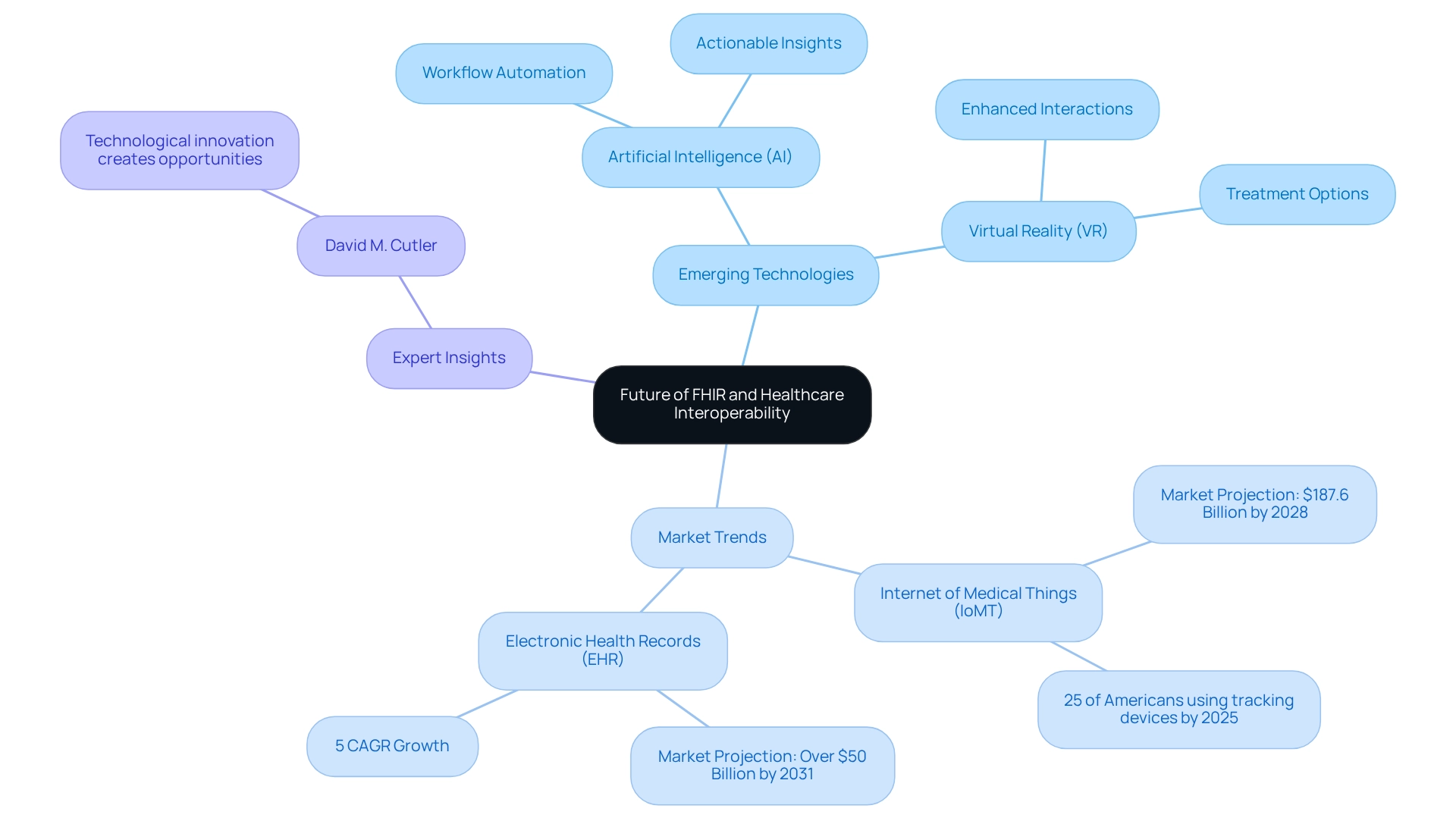
The future of health information exchange interoperability, particularly regarding FHIR interoperability, is exceptionally bright. Continuous innovations are driving efforts to enhance healthcare connectivity. Emerging technologies, especially artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR), are set to transform information exchange processes, significantly improving efficiency and patient outcomes. For instance, the integration of health information standards with wearable devices and telehealth solutions is expected to elevate functionality, enabling real-time health monitoring and information sharing. This capability is crucial, especially as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) market is projected to reach $187.6 billion by 2028.
As healthcare systems increasingly adopt FHIR interoperability, the importance of AI and machine learning escalates. These technologies facilitate workflow automation, enhance seamless information connectivity, and generate actionable insights, addressing nearly 40% of significant errors found in medical records. The advancements in digital medicine, as highlighted at the Interface Summit, demonstrate how AI can act as a trusted advisor, improving interactions and treatment options.
David M. Cutler asserts that “technological innovation… is creating opportunities for stakeholders across segments by automating workflows, promoting data connectivity and interoperability, and generating actionable insights.” Furthermore, the anticipated growth in the electronic health records (EHR) market, expected to surpass $50 billion by 2031, underscores the critical role of interoperability in enhancing patient experiences and reducing errors.
Looking ahead to 2025, trends indicate that standards will continue to evolve, adapting to new challenges and opportunities within the medical landscape. The synergy of AI and VR with FHIR applications will not only enhance FHIR interoperability but also streamline processes across various medical sectors. As healthcare providers increasingly rely on these technologies, the potential for improved care and operational efficiency will be substantial, paving the way for a more connected and responsive medical system.
Moreover, as emphasized at the Interface Summit, the ownership and accessibility of health data are crucial. Empowering patients with control over their health information is essential for unlocking the full potential of these innovations. Arvato is committed to spearheading this transformative journey.
Best Practices for Implementing FHIR: A Guide for Healthcare Professionals
To effectively implement FHIR in healthcare settings, professionals must adhere to several best practices that ensure a smooth integration process:
-
Assess Current Systems: Begin with a thorough evaluation of existing systems to identify potential integration points for the health information standard. This essential step is vital for understanding how the standard can enhance existing workflows and information management. The timeline for medical test orders, spanning from 1950 to 2021, underscores the evolution of information management in the medical field, highlighting the pressing need for contemporary integration solutions.
-
Engage Stakeholders: Actively involve key stakeholders, including IT personnel, clinical teams, and administrative staff. Their insights and support are crucial for aligning goals and ensuring that the integration meets the needs of all users. Successful pilot projects have shown that organizations engaging stakeholders experience higher success rates in their FHIR initiatives. Utilizing structured requirements management can transform unstructured information into a clear hierarchical model, ensuring that all stakeholder needs are effectively addressed.
-
Prioritize Security: Given the sensitivity of healthcare information, implementing robust security measures is non-negotiable. Organizations must safeguard patient information throughout the integration process, adhering to industry standards and regulations. As highlighted by Edenlab, “ClickHouse assists us in effectively and dependably examining logs spanning trillions of internet requests to detect harmful traffic and provide clients with comprehensive analytics,” emphasizing the critical nature of information management and security in healthcare integration. Furthermore, Avato’s solutions are designed to support regulatory compliance and security audits, ensuring that organizations can meet industry standards.
-
Start Small: Initiate healthcare data integration with pilot projects. This approach allows organizations to test the waters, identify challenges, and refine processes before scaling up to broader implementations. Successful pilot initiatives have demonstrated significant enhancements in information accessibility and FHIR interoperability. For instance, establishing a health information registry can standardize resource models, promote best practices, and minimize the risk of varied implementations. Leveraging XSLT can streamline the transformation of XML information, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency during this phase.
-
Stay Informed: The healthcare information exchange landscape is continually evolving. Keeping abreast of updates and industry trends empowers organizations to leverage new features and improvements, ensuring their integration remains relevant and effective. A sophisticated user interface designed for data retrieval and analysis can significantly enhance user experience, showcasing the value of user-friendly systems in the context of integration. Additionally, employing schemas can substantially reduce programming errors, leading to cost savings and more reliable integration outcomes.
By adhering to these best practices, medical organizations can optimize the advantages of FHIR interoperability, ultimately enhancing overall patient care. Notably, successful pilot projects have demonstrated that organizations that involve stakeholders and emphasize security experience greater success rates in their health data initiatives. As the healthcare sector advances towards more integrated systems, these strategies will be essential for navigating the complexities of FHIR integration.
For further insights and resources, consider exploring Avato’s offerings to support your integration journey.
Conclusion
The exploration of Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) underscores its pivotal role in transforming healthcare data exchange and enhancing interoperability among diverse systems. By addressing the challenges of fragmented data, FHIR facilitates efficient access to patient information and empowers healthcare providers to deliver high-quality care. As organizations increasingly recognize the significance of FHIR, its adoption is poised to rise, driven by the demand for streamlined operations and improved patient outcomes.
The evolution of FHIR from previous standards marks a crucial shift towards user-friendly and adaptable solutions, ensuring that healthcare systems can meet the demands of modern data sharing. With its modular architecture and RESTful APIs, FHIR simplifies data management and integration, making it essential for achieving seamless communication across platforms. Real-world applications illustrate how FHIR enhances patient care and engagement, showcasing its potential to revolutionize the healthcare landscape.
However, challenges such as security and privacy concerns must be addressed for successful FHIR implementation. Organizations must prioritize compliance with regulations while adopting robust security measures to protect sensitive patient data. By navigating these challenges and following best practices, healthcare professionals can leverage FHIR to maximize interoperability and improve patient care.
Looking ahead, the future of FHIR is bright, with emerging technologies like AI and VR poised to further enhance its capabilities. As healthcare continues to evolve, FHIR will play a central role in creating a more connected and efficient system. Embracing FHIR not only represents a commitment to innovation but also signifies a crucial step towards a more integrated and responsive healthcare environment, ultimately benefiting patients and providers alike.

