Overview
We recognize the critical importance of strengthening hospital IT infrastructure. Our article delves into four essential practices that can significantly enhance security:
- Identifying vulnerabilities
- Implementing robust cybersecurity measures
- Establishing continuous monitoring
- Conducting staff training
These practices are not merely theoretical; they are supported by compelling evidence and real-world examples. For instance, regular evaluations are crucial for uncovering security weaknesses, while multi-layered security strategies effectively prevent unauthorized access. Furthermore, ongoing staff training has a proven impact on reducing phishing attempts. Together, these elements contribute to a comprehensive approach to safeguarding healthcare IT systems.
It’s time to take action—let us partner with you to fortify your IT infrastructure against emerging threats.
Introduction
In an era where cyber threats loom larger than ever, we find ourselves at a critical juncture in the healthcare sector, grappling with the dual challenge of protecting sensitive patient data while ensuring operational integrity. As we increasingly rely on technology, the vulnerabilities within our IT infrastructures become more pronounced, necessitating a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
From conducting regular security assessments to implementing robust multi-layered defense strategies, we must prioritize our cybersecurity measures. This article delves into essential strategies for enhancing hospital IT security, highlighting the importance of:
- Continuous monitoring
- Staff training
- Adoption of advanced technologies to safeguard against ever-evolving threats
By addressing these key areas, we can not only protect our systems but also foster a culture of security awareness that empowers every employee to contribute to a safer healthcare environment.
Identify Vulnerabilities in Hospital IT Infrastructure
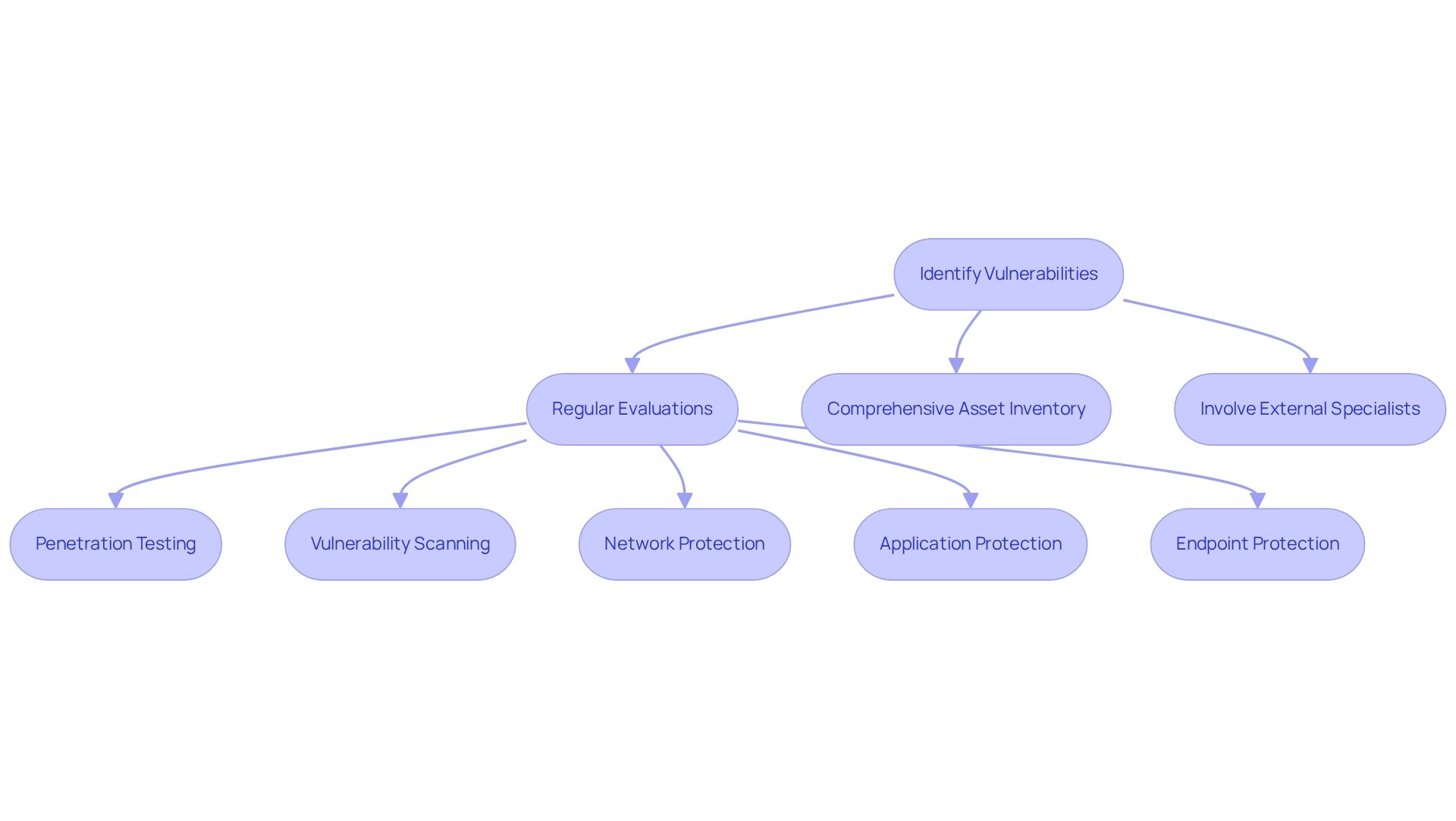
To effectively identify weaknesses in our hospital IT infrastructure, we must prioritize regular evaluations that include penetration testing and vulnerability scanning. These evaluations focus on essential areas, including:
- Network protection
- Application protection
- Endpoint protection
Furthermore, maintaining a comprehensive inventory of all hardware and software assets is crucial for identifying outdated or unsupported systems that require our attention. Involving external specialists provides an unbiased viewpoint on possible weaknesses, allowing us to prioritize corrective actions according to risk levels.
For instance, a recent vulnerability evaluation at one of our healthcare centers uncovered obsolete software on various medical devices, prompting prompt updates that significantly improved our protective stance. In 2025, statistics reveal that only 45% of healthcare facilities perform regular safety evaluations, highlighting the necessity for enhanced methods in this vital domain.
Cybersecurity specialists emphasize that regular vulnerability evaluations are crucial for protecting patient privacy and preserving the integrity of hospital IT infrastructure against emerging threats. As Derek Manky, Chief Security Strategist and Global Vice President of Threat Intelligence, notes, “As a result, threat actors are executing targeted attacks quickly and more precisely.” This underscores the necessity for us to implement strong protective measures.
Moreover, the case study on detrimental bot traffic in healthcare demonstrates the significant security risks presented by automated threats, emphasizing the need for regular evaluations to safeguard patient privacy and infrastructure integrity.
Implement Robust Cybersecurity Measures
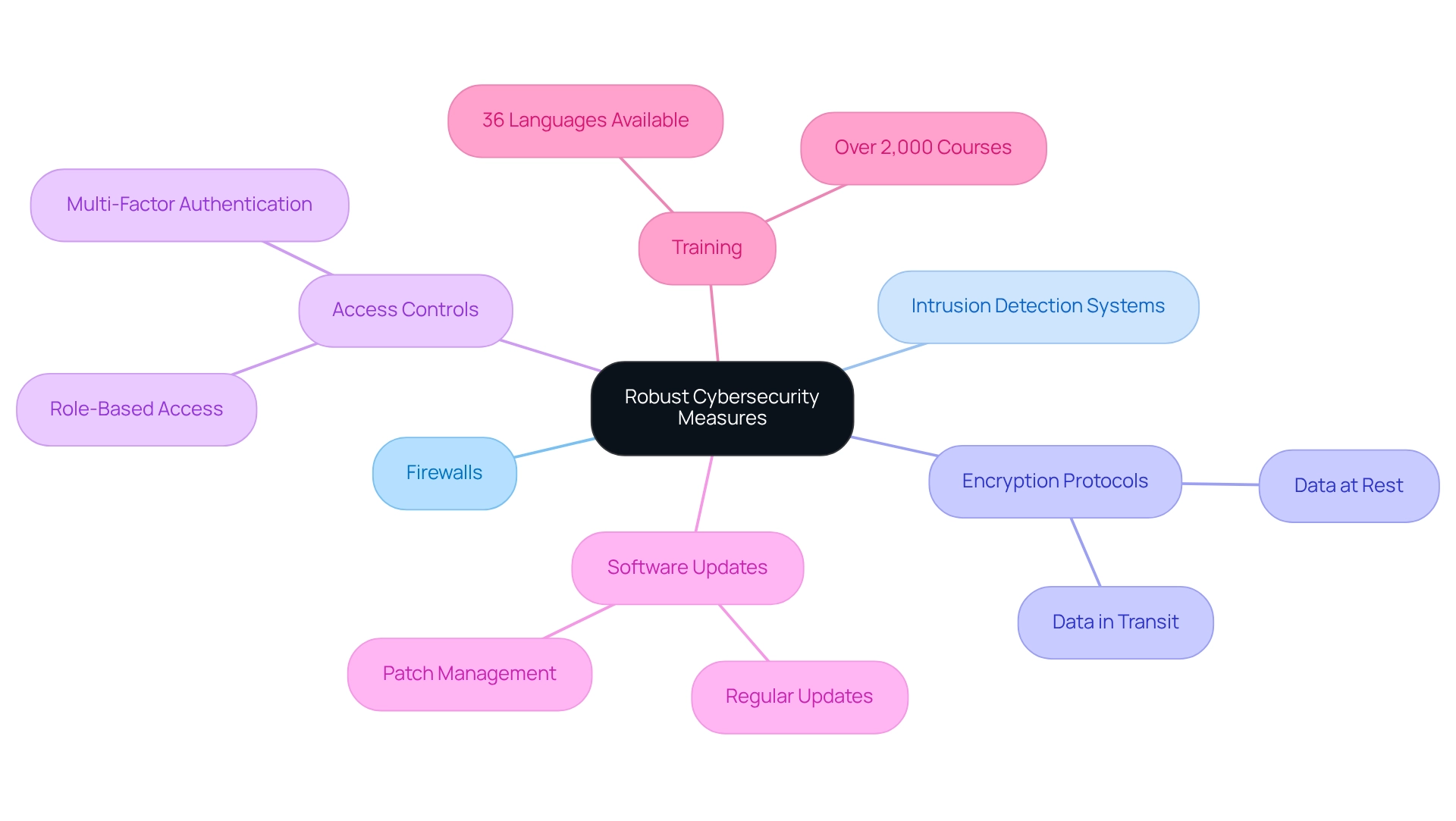
To safeguard sensitive patient information and maintain operational integrity, we must adopt a multi-layered security strategy. This comprehensive approach encompasses:
- Firewalls
- Intrusion detection systems
- Robust encryption protocols for data both at rest and in transit
Strong access controls, including role-based access and multi-factor authentication, are essential to prevent unauthorized access to critical information. Furthermore, regular software updates and diligent patch management are crucial for mitigating risks associated with known vulnerabilities.
As Robbie Sinclair aptly stated, “Security is always excessive until it’s not enough,” underscoring the critical need for comprehensive protective measures. For instance, a healthcare organization that implemented a zero-trust architecture reported a marked decrease in unauthorized access attempts, highlighting the effectiveness of such strategies. As cyber threats continue to escalate—evidenced by a 30% surge in global cyber attacks in Q2 2024, averaging 1,636 weekly attacks per organization—we must prioritize these best practices to enhance our security posture. Moreover, with the digital security market projected to reach $212 billion by the end of 2025, investing in advanced safety measures is not merely prudent; it is essential for the future of healthcare. To support this initiative, we can access over 2,000 training courses in 36 languages, enhancing our awareness and protection against emerging online security threats. This ongoing education is vital for sustaining a robust cybersecurity framework, ensuring that our medical facilities are well-equipped to tackle the challenges ahead.
Establish Continuous Monitoring and Real-Time Alerts
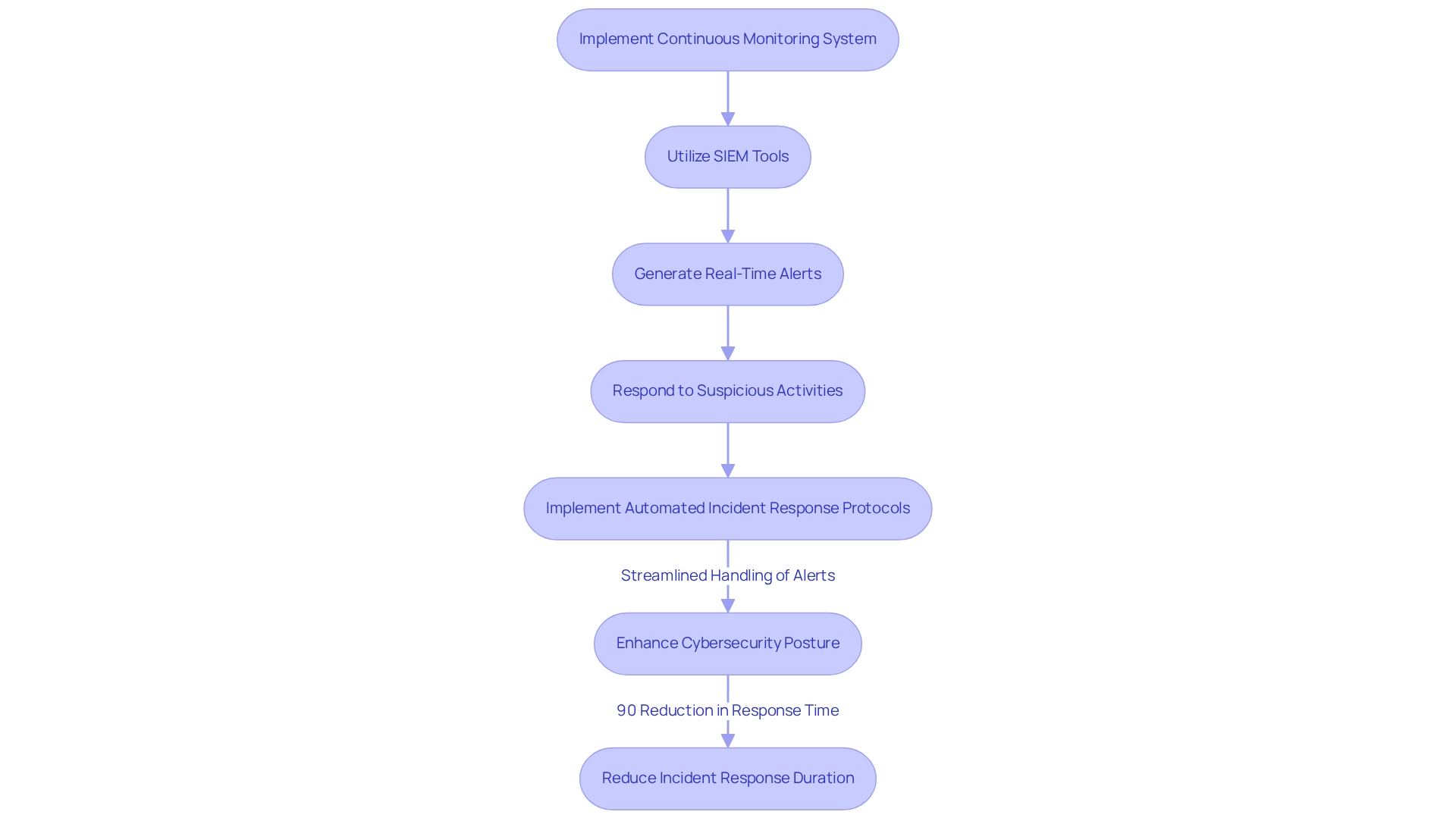
Implementing a continuous monitoring system is not just beneficial; it is essential for enhancing the hospital IT infrastructure protection in healthcare facilities. We utilize information and event management (SIEM) tools that collect and assess safety-related data from across our IT infrastructure. These tools are designed to generate real-time alerts for suspicious activities, enabling us to respond swiftly to potential threats. For instance, we have seen healthcare facilities that integrated a SIEM solution successfully detect and mitigate ransomware attacks within minutes, significantly reducing potential damage.
The advantages of continuous monitoring extend far beyond immediate threat detection. By implementing automated incident response protocols, we can streamline the handling of alerts, ensuring our security teams focus on critical issues instead of being overwhelmed. Statistics suggest that by 2025, healthcare facilities employing continuous monitoring tools will observe a substantial enhancement in their cybersecurity posture, with many noting a decrease in incident response durations by as much as 90%, according to industry reports.
Expert insights underscore the significance of these frameworks in safeguarding sensitive patient information. As one IT security professional aptly stated, “With the right tools in place, we can just flip the switch, and turn out the lights,” emphasizing the ease with which hospitals can transition to a more secure environment using SIEM tools. Case studies, such as the UMass Memorial Health Care data storage upgrade, illustrate the importance of modernizing hospital IT infrastructure to mitigate risks associated with outdated technologies. The previous hospital IT infrastructure had reached its end of life, resulting in increased costs and data management risks, which further underscores the necessity for robust continuous monitoring solutions in healthcare settings. This upgrade not only improved data management but also aligned with the implementation of continuous monitoring systems to enhance overall security.
Conduct Staff Training and Awareness Programs
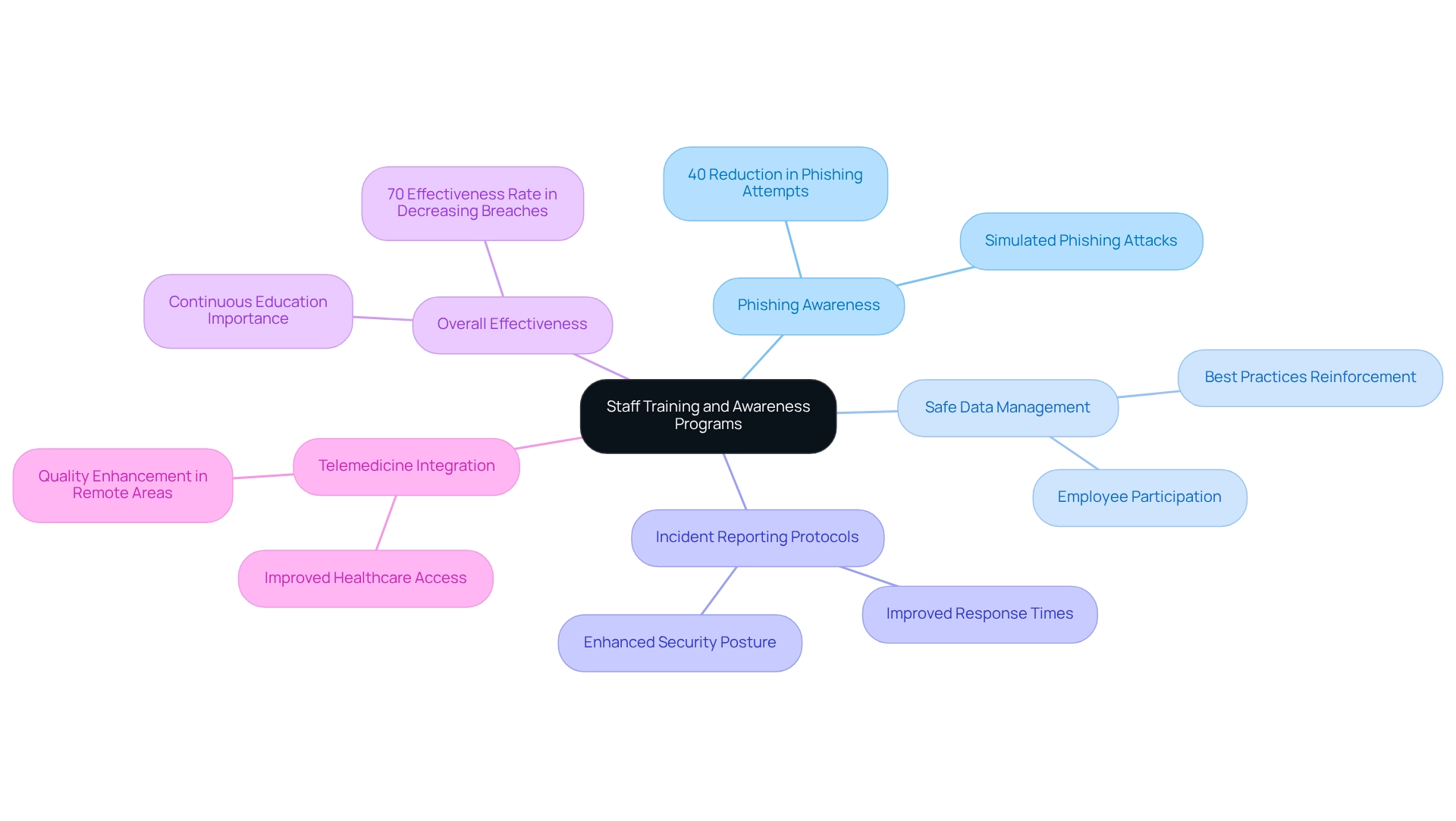
To enhance medical facility security, we must establish thorough training initiatives that encompass:
- Phishing awareness
- Safe data management
- Incident reporting protocols
Regular training sessions, complemented by simulated phishing attacks, significantly bolster staff vigilance and reinforce best practices. For instance, a medical facility that instituted quarterly training sessions observed a remarkable 40% reduction in successful phishing attempts, underscoring the effectiveness of continuous education. According to recent statistics, our training programs in hospitals have demonstrated a 2025 effectiveness rate of over 70% in decreasing breaches.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of security awareness empowers our employees to actively participate in safeguarding sensitive information, ultimately strengthening the overall security posture of our institution. As Lee et al. noted, effective training is crucial for adapting to the evolving landscape of cyber threats. Moreover, the introduction of telemedicine services in Nepal emphasizes how effective training and technology integration can greatly enhance healthcare access and quality, illustrating the wider effects of security training.
Prioritizing our staff training is not just beneficial but imperative for maintaining robust cybersecurity in healthcare settings.
Conclusion
Enhancing hospital IT security is not just important; it is imperative in the face of escalating cyber threats. Regular security assessments are crucial as they help us identify vulnerabilities in our IT infrastructure, enabling targeted remediation. By engaging third-party experts, we gain essential insights that fortify our critical systems against potential attacks.
Robust cybersecurity measures are vital for protecting sensitive patient data. We advocate for a multi-layered strategy that incorporates firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and stringent access controls, significantly reducing risks. As cyber threats continue to evolve, ongoing education and timely software updates are indispensable for maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture.
Establishing continuous monitoring and real-time alerts is essential for effective threat detection. Security information and event management tools facilitate the rapid identification of potential threats, allowing us to minimize damage and safeguard sensitive information.
Moreover, cultivating a culture of security awareness through comprehensive training empowers our staff to recognize and respond to cyber threats effectively. This proactive approach not only strengthens the overall security posture of our healthcare institutions but also equips our employees to navigate the complex landscape of cybersecurity risks.
In conclusion, a proactive and multifaceted approach to cybersecurity is essential for healthcare organizations like ours. By prioritizing vulnerability assessments, implementing robust measures, establishing continuous monitoring, and investing in staff training, we can create a secure environment that protects sensitive data. The urgency to act is clear; safeguarding patient information and maintaining operational integrity is paramount.

