Overview
Best practices for ESB architecture are crucial for organizations aiming to achieve seamless integration. By defining clear objectives, embracing loose coupling, utilizing standard protocols, implementing robust monitoring tools, and planning for scalability, organizations can significantly enhance their performance.
These strategies not only reduce costs but also ensure adaptability to future demands. Real-world implementations across various industries demonstrate the effectiveness of these approaches. Therefore, it is imperative for organizations to adopt these best practices to thrive in an increasingly complex environment.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of enterprise technology, the necessity for seamless integration among diverse applications has reached unprecedented levels. Enter the Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)—a formidable middleware solution that serves as a central hub for communication, enabling various systems to interact without direct connections. This architecture not only promotes loose coupling, allowing systems to evolve independently, but also significantly enhances operational efficiency and agility.
As organizations strive to keep pace with shifting business demands, the adoption of ESB architecture, particularly through innovative platforms like Avato, emerges as a strategic imperative. With proven benefits ranging from improved integration efficiency to substantial cost reductions, the significance of ESB in navigating the complexities of digital transformation cannot be overstated.
Are you ready to embrace this transformative technology and position your organization for success?
Understanding Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) Architecture
An Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) serves as a pivotal middleware framework that streamlines communication among diverse applications and services within an organization. Acting as a centralized hub, it allows various systems to interact without requiring direct connections, thus promoting loose coupling. This architecture empowers systems to evolve independently while ensuring seamless integration across the enterprise landscape.
Key components of an ESB encompass:
- Message routing
- Data transformation
- Protocol mediation
These elements work in unison to enhance the agility and scalability of enterprise applications, enabling organizations to adapt to changing business demands. Recent statistics indicate that entities employing ESB architecture have witnessed a remarkable boost in operational efficiency, with many reporting a reduction in connection complexity by up to 40%.
The advantages of utilizing an ESB are underscored by industry leaders who emphasize its critical role in facilitating smoother integration processes. For example, a recent survey revealed that 68% of organizations using ESB reported enhanced system interoperability and shorter time-to-market for new services. Furthermore, real-world instances highlight the efficacy of ESB middleware architecture; companies in sectors such as banking and healthcare have effectively leveraged ESB to integrate legacy systems with modern applications, resulting in improved service delivery and customer satisfaction.
In this context, the Hybrid Integration Platform emerges as a specialized solution for simplifying complex integrations and maximizing the value of legacy systems. By unlocking isolated assets and enabling seamless data flow, this platform empowers financial institutions to spearhead the AI revolution and future-proof their operations. With real-time monitoring and alerts on system performance, this solution significantly reduces costs while bolstering operational efficiency.
In the realm of cloud solutions, it is noteworthy that half of surveyed businesses have transitioned to the cloud for disaster recovery, underscoring the relevance of ESB in managing these shifts. However, 32% of cloud budgets are wasted, highlighting the importance of effective integration solutions such as Avato’s hybrid platform in optimizing cloud expenditures. Additionally, SMEs are projected to allocate over 50% of their technology budgets to cloud services in 2023, reflecting the growing trend toward cloud-based solutions and its implications for ESB adoption.
Recent advancements in ESB technology have further fueled its increasing adoption. With global spending on public clouds anticipated to approach nearly $600 billion, organizations are progressively recognizing the advantages of cloud-based ESB solutions that offer flexibility and scalability. Case studies reveal that businesses embracing ESB architecture have not only refined their connection processes but also achieved substantial cost savings, with some reporting reductions in operational expenses by as much as 30%.
As Gustavo Estrada articulated, “The system has the capability to streamline intricate projects and provide outcomes within preferred timelines and financial limitations,” demonstrating the efficiency of solutions like ESB in achieving organizational goals.
In summary, the benefits of employing an ESB within organizations are extensive, ranging from enhanced operational efficiency to improved agility in responding to market demands. As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of digital transformation, the adoption of ESB architecture, particularly through a hybrid platform, emerges as a best practice for ensuring effective connectivity.
Key Benefits of Implementing an ESB
Implementing an ESB architecture offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance organizational operations, particularly in sectors like banking where connectivity efficiency is paramount. Avato’s hybrid unification platform exemplifies these advantages, providing speed, security, and simplicity in system connections. Key advantages include:
- Enhanced Connectivity Efficiency: The ESB architecture facilitates seamless connections among various applications, drastically reducing the time and resources needed to link different systems. This efficiency is critical; studies indicate that 24% of supply chain firms incur losses exceeding $500K annually due to inadequate connections. By adopting the ESB architecture, banking institutions can mitigate these losses through effective integration strategies, as evidenced by successful implementations across various financial institutions, including a notable 30% reduction in integration time at Coast Capital.
- Enhanced Scalability: As companies grow, an ESB architecture can effortlessly accommodate new applications and services, allowing for expansion without extensive reconfiguration. The platform supports a registry of data services, ensuring that businesses can adapt to evolving demands without disruption. This adaptability has been crucial for clients like Coast Capital during significant system transitions, enabling them to onboard new services within weeks instead of months.
- Cost Reduction: By centralizing connection processes, organizations can significantly lower operational expenses associated with maintaining multiple point-to-point links. The implementation of ESB architecture not only streamlines operations but also alleviates the financial burden of integration, making it a cost-effective solution for modern enterprises. This was particularly evident in the team’s collaboration with Coast Capital, where they facilitated major transitions with minimal downtime, resulting in a 20% reduction in operational costs.
- Enhanced Agility: The ESB architecture empowers organizations to respond swiftly to changing business requirements, facilitating the rapid introduction of new services and applications. This agility is essential in today’s fast-paced environment, where the ability to pivot quickly can determine competitive advantage. The hybrid platform from the company has demonstrated its capacity to enhance operational capabilities, enabling clients to effectively respond to market changes, as noted by Tony Leblanc from the Provincial Health Services Authority, who praised the firm’s responsiveness and professionalism.
- Better Data Management: With integrated data transformation capabilities, ESBs ensure smooth data flow between systems, enhancing data quality and consistency. This improved data management is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage their data for strategic decision-making within an ESB architecture. The platform is designed for secure transactions, establishing it as a reliable choice for banks and healthcare organizations.
A case study on real-time data coordination architecture effectively illustrates these advantages. By utilizing the ESB architecture to manage data interfaces, companies can safely and effectively coordinate data movement, ensuring that data is modified and conveyed among different technologies and applications without compromising security.
Moreover, IT managers have observed that the efficiency gained through ESB implementation not only streamlines intricate projects but also delivers outcomes within targeted timelines and financial limits. As Gustavo Estrada emphasizes, organizations benefit from the ability to simplify complex unification tasks through ESB architecture, ultimately resulting in enhanced operational capabilities and reduced expenses. In summary, the deployment of Avato’s ESB architecture, established in 2010, represents a strategic initiative for businesses seeking to improve connectivity efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall agility in their operations.
Common Challenges in ESB Architecture
While Enterprise Service Buses (ESBs) offer numerous advantages for integration, organizations often encounter significant challenges during their implementation.
Complexity of Integration: The design and configuration of an ESB can be intricate, necessitating skilled personnel and meticulous planning. This complexity can lead to delays and increased costs if not managed effectively. To enhance collaboration strategies, engaging stakeholders early in the process is essential to ensure that requirements are accurately captured from the outset. Additionally, modeling business processes and activity flows is vital to visualize the current and ideal states, aiding in aligning stakeholder expectations.
Single Point of Failure: Without adequate redundancy, an ESB can become a significant weakness, functioning as a single point of failure that jeopardizes the entire connectivity framework. Data indicates that many organizations experience disruptions due to this oversight, underscoring the importance of robust design practices and future-proofing systems to integrate new tools seamlessly with existing assets. The company employs specific strategies to ensure redundancy and resilience in its solutions.
Performance Issues: As the number of integrated applications increases, performance can suffer if the ESB is not optimized. Organizations must ensure that their ESB can handle growing demands without compromising service quality. The company’s commitment to guaranteeing round-the-clock uptime for essential connections highlights its dependability in addressing these performance challenges. Continuous monitoring and analytics capabilities are crucial to optimizing operations and enhancing customer experiences. The analytics tools provided by this company offer practical insights that assist organizations in identifying bottlenecks and improving overall performance.
Resistance to Change: Employees may resist the adoption of new connection technologies, which can impede progress. Effective change management strategies are critical to facilitating smooth transitions and encouraging acceptance of new systems. Educating personnel about the advantages and features of the hybrid connection platform can significantly enhance flexibility and reduce opposition.
Integration with Legacy Systems: Connecting outdated systems to a modern ESB often presents technical challenges, necessitating additional resources and specialized expertise. This is particularly relevant in sectors like banking, healthcare, and government, where legacy systems are prevalent. The hybrid connectivity platform has proven essential in streamlining these complex projects, enabling companies in these sectors to achieve their objectives within specified timelines and financial constraints.
Real-world examples illustrate how organizations have successfully navigated these complexities. Clients have observed that this approach not only enhances operational capabilities but also significantly reduces costs related to system integration. As Gustavo Estrada stated, “This entity has the ability to simplify complex projects and deliver results within desired time frames and budget constraints.”
Expert insights emphasize the necessity of proactively addressing these challenges. Integration specialists often highlight the importance of designing ESBs with built-in redundancy to mitigate the risk of single points of failure. Furthermore, ongoing performance monitoring is crucial to ensure that the ESB can adapt to changing demands and maintain optimal functionality.
In summary, although adopting ESB architecture may present difficulties, companies can overcome these challenges through meticulous planning, strategic resource allocation, and utilizing advanced platforms like Avatar that are designed to effectively tackle these complexities. Additionally, the application segment of the Enterprise Service Bus market encompasses various sectors, each offering specific opportunities shaped by market demands, further emphasizing the relevance of robust ESB architecture.
Best Practices for Designing ESB Architecture
To design an effective Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) architecture, organizations must adhere to several best practices that ensure success:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establishing specific collaboration goals is crucial for guiding the design and implementation process. Clear objectives streamline efforts and enhance the likelihood of achieving reliable performance. The organization’s commitment to guaranteeing round-the-clock uptime for essential connections underscores the significance of clear objectives in attaining successful results, particularly in industries such as banking where dependability is paramount.
- Embrace Loose Coupling: Designing services to interact without being tightly bound is essential for enhancing flexibility and maintainability. Loose coupling allows for independent service updates and modifications, thereby reducing the risk of widespread disruptions. Experts emphasize that this method fosters a more flexible unification atmosphere, enabling entities to respond swiftly to evolving business requirements—a principle embodied by Avato in its hybrid unification solutions.
- Utilize Standard Protocols: Adopting widely accepted communication protocols ensures compatibility and simplifies unification efforts. By leveraging standards such as HTTP, REST, and SOAP, entities can facilitate smoother interactions between disparate systems, ultimately reducing integration time and costs. The platform supports these standards, enhancing seamless and secure data connectivity.
- Implement Monitoring and Management Tools: Utilizing real-time monitoring tools is vital for tracking performance and proactively identifying issues. Continuous oversight enables organizations to address performance bottlenecks early, preventing potential disruptions in production environments. For instance, DriveTime’s transition to an ESB architecture facilitated real-time updates of sales data, significantly improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. As Justin Miller, Senior Director at DriveTime, noted, “This shift not only improved operational efficiency but also enhanced customer satisfaction by providing up-to-date information and quicker service.” The platform offers robust monitoring features, including comprehensive analytics and notifications, to ensure ongoing reliability and meet the specific needs of complex systems.
- Plan for Scalability: Designing the architecture with future growth in mind is essential. An effective ESB architecture should accommodate increased loads and new applications without requiring extensive rework. This foresight not only supports continuous business growth but also ensures that the unification framework remains robust and adaptable, aligning with the company’s mission to maximize legacy system value and simplify intricate connections.
By adhering to these optimal methods, organizations can establish a robust ESB architecture that not only meets current connectivity needs but also positions them for future success in a constantly evolving technological landscape, supported by a dedicated hybrid connection platform. The company, named after the Hungarian term for “of dedication,” exemplifies a profound commitment to architecting the technological foundation necessary to power rich, connected customer experiences, ultimately unlocking isolated assets and enabling business value creation.
Integrating ESB with Microservices: A Modern Approach
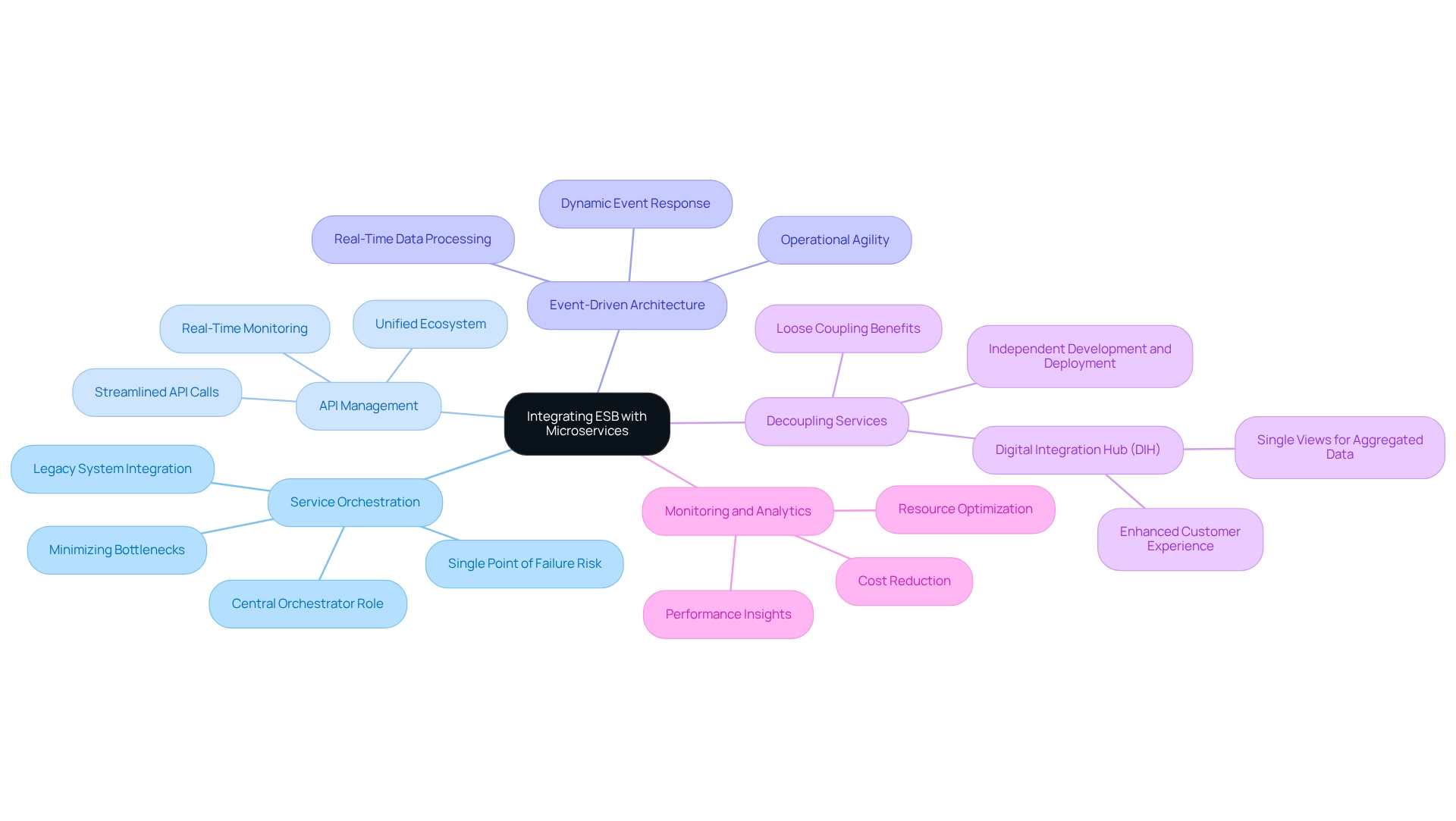
Combining an ESB architecture with microservices establishes a robust framework for modern application development, particularly when leveraging a specialized hybrid connectivity platform. What are the essential considerations for effectively utilizing this combination?
- Service Orchestration: The ESB functions as a central orchestrator for microservices, adeptly managing interactions and data flows. This orchestration is vital for ensuring that services collaborate seamlessly, minimizing the risk of bottlenecks and enhancing overall system performance. The platform excels in this domain, significantly simplifying complex integrations and enabling businesses to maximize the value of their legacy systems. However, it is crucial to recognize that an ESB can also serve as a single point of failure for the entire enterprise, which poses risks to overall availability.
- API Management: By employing the ESB for API management, organizations can streamline API calls, facilitating seamless communication between microservices and external systems. This capability is essential for maintaining a unified ecosystem where data circulates freely and securely, further enhanced by real-time monitoring and alert features.
- Event-Driven Architecture: Implementing an event-driven architecture empowers the ESB to respond dynamically to events generated by microservices. This approach fosters real-time data processing, enabling businesses to react swiftly to evolving conditions and customer needs, thereby enhancing operational agility. The platform supports this agility, ensuring 24/7 uptime and reliability, which is particularly critical in sectors such as banking, healthcare, and government.
- Decoupling Services: Maintaining loose coupling between microservices and the ESB is essential for promoting flexibility and minimizing dependencies. This decoupling allows teams to develop, deploy, and scale services independently, which is especially advantageous in rapidly evolving environments. The Digital Integration Hub (DIH) architecture exemplifies this approach, supporting the creation of Single Views for aggregated data, which enhances customer experience and operational reliability.
- Monitoring and Analytics: The monitoring capabilities of the ESB provide valuable insights into the performance of microservices. By analyzing these metrics, organizations can optimize resource distribution and identify areas for improvement, ensuring that the amalgamation remains efficient and effective. Avato’s hybrid unification platform significantly reduces costs while delivering these insights, enabling businesses to secure their operations for the future.
As organizations increasingly adopt microservices, the integration of ESB architecture with these frameworks is becoming a strategic necessity. By 2025, trends indicate that enterprises will continue to leverage ESB for service orchestration, particularly as they confront growth challenges and seek enhanced scalability. The effectiveness of service orchestration using ESB architecture is underscored by case studies demonstrating improved operational reliability and performance, making it a preferred choice for companies aiming to elevate customer experiences and adapt to market demands.
Industry leaders emphasize that bridging the gap between technological advancement and business value is essential for real-time data streaming, processing, and analytics. This highlights the significance of a well-executed ESB in contemporary unification strategies. As noted by Kai Waehner, this integration is crucial for maximizing the value derived from technological advancements. Avato’s commitment to architecting the technology foundation necessary to power rich, connected customer experiences is evident in these strategies.
Real-World Examples of Successful ESB Implementations
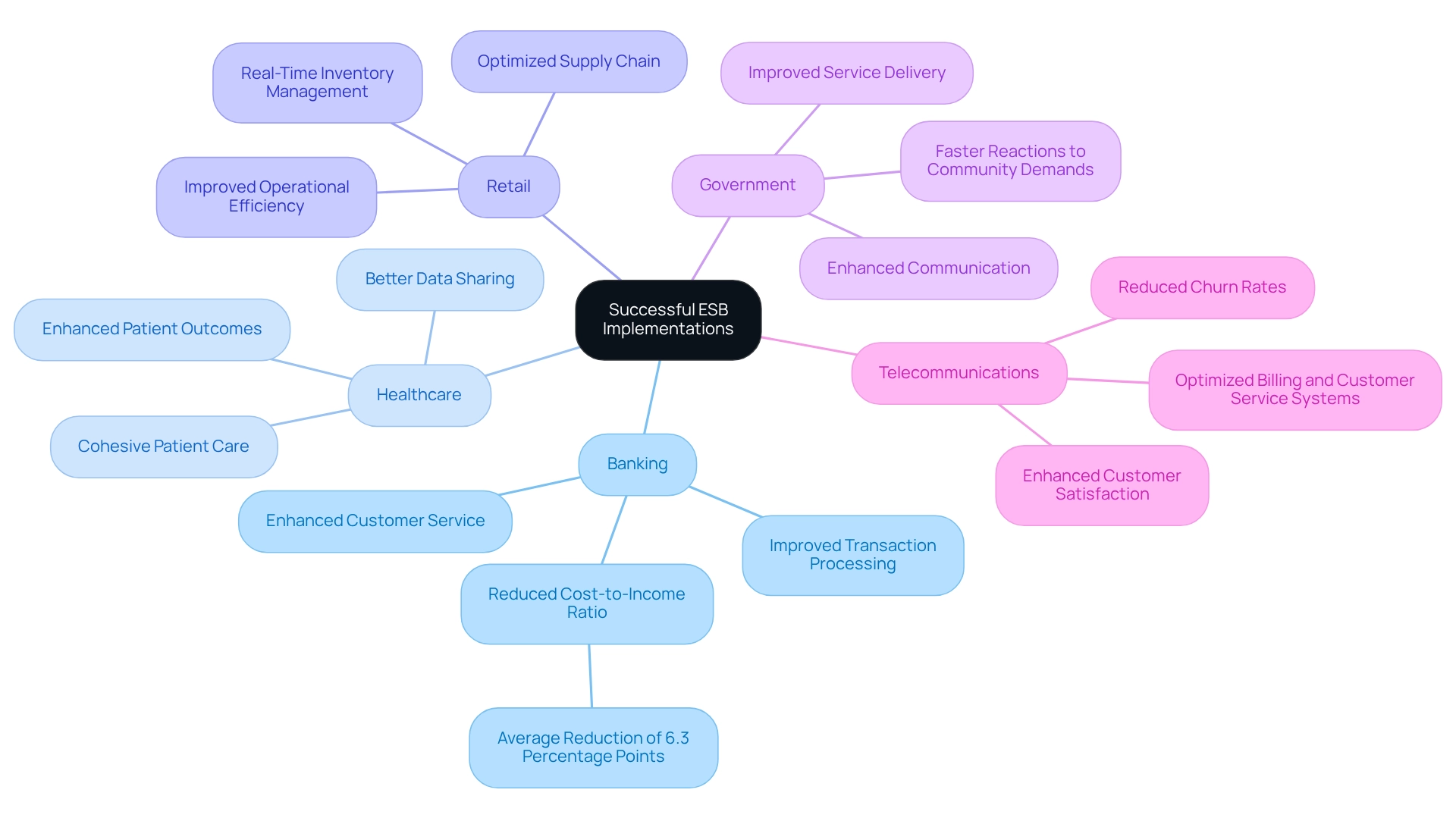
Numerous organizations have effectively adopted ESB architecture, showcasing its transformative impact across various sectors. In the banking sector, a prominent bank successfully integrated its legacy systems with an ESB architecture, resulting in significantly improved transaction processing times and enhanced customer service. This combination not only streamlined operations but also led to a decrease in the bank’s cost-to-income ratio by an average of 6.3 percentage points over three years, highlighting the financial advantages of effective data collaboration.
Furthermore, the incorporation of generative AI has further improved customer experience, particularly through the development of sophisticated chatbots and virtual assistants. This reflects the banking sector’s response to evolving consumer expectations for seamless service across digital and physical touchpoints. Avato’s support for 12 levels of interface maturity guarantees that banks can balance speed of incorporation with the sophistication needed to future-proof their technology stack.
In healthcare, a provider leveraged ESB architecture to connect disparate patient management systems, facilitating better data sharing and ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. This combination enabled a more cohesive approach to patient care, ensuring that healthcare professionals had access to critical information when needed. As Gustavo Estrada noted, ‘Avato has the ability to simplify complex projects and deliver results within desired time frames and budget constraints,’ which underscores the effectiveness of ESB implementations in healthcare.
In retail, a major retailer implemented ESB architecture to optimize its supply chain operations, enabling real-time inventory management. This strategic move not only reduced operational costs but also enhanced the retailer’s ability to respond to market demands swiftly, improving overall efficiency.
Additionally, a government agency adopted ESB architecture to enhance communication between various departments, resulting in improved service delivery and operational efficiency. This merger promoted a more cooperative atmosphere, enabling faster reactions to community demands.
In telecommunications, a telecom company utilized ESB architecture to integrate its billing and customer service systems, which led to enhanced customer satisfaction and reduced churn rates. By optimizing these essential functions, the company was able to offer a more fluid experience for its customers.
These case studies demonstrate the adaptability and efficiency of ESB architecture in promoting success across various industries. Avato’s dedication to guaranteeing round-the-clock availability for essential connections not only improves reliability but also bolsters the transformative initiatives mentioned—especially in the financial services industry where generative AI is transforming trading, customer engagement, and security.
The Future of ESB Architecture: Trends and Innovations
Several pivotal trends and innovations are significantly influencing the future of ESB architecture.
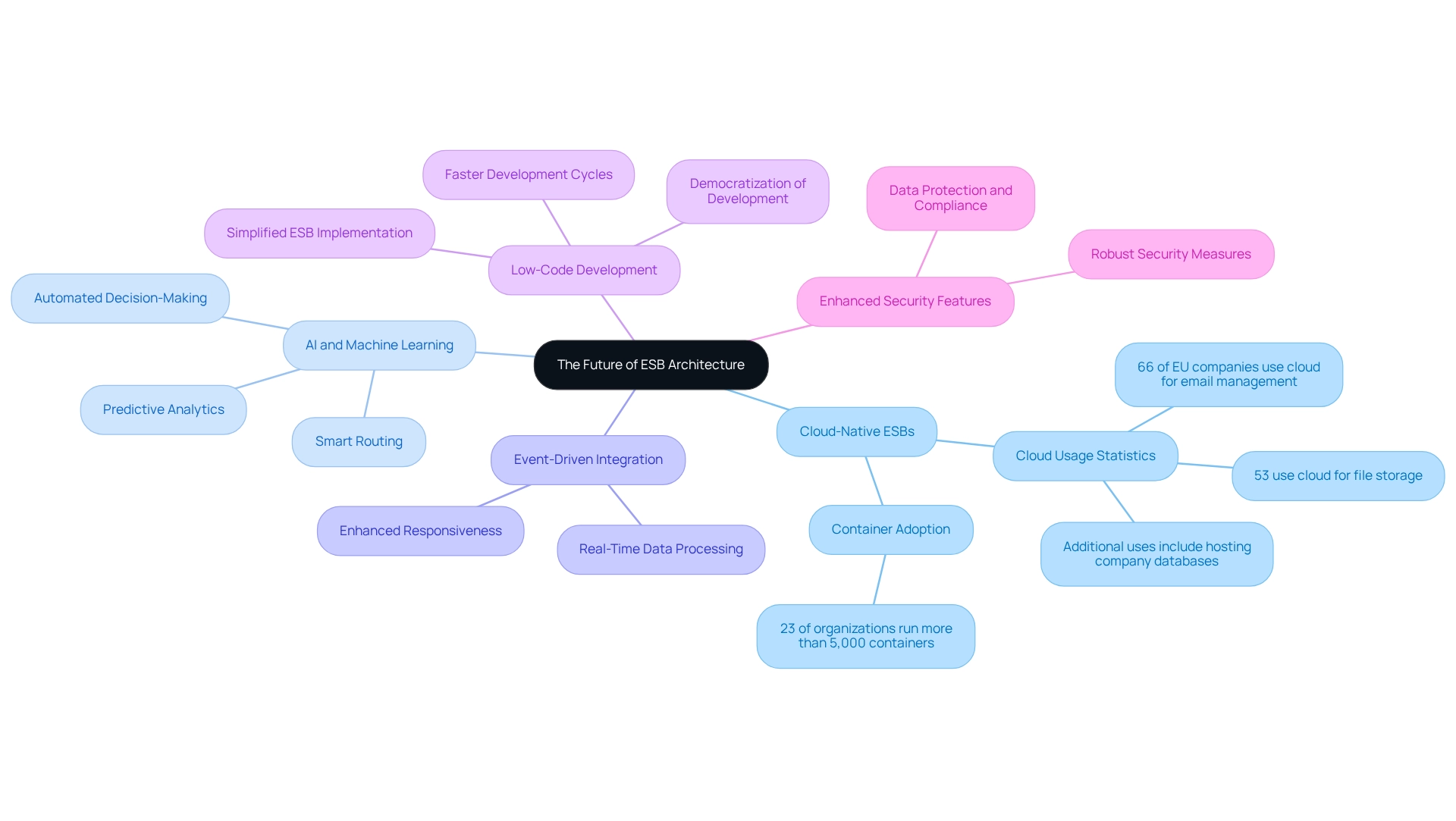
Cloud-Native ESBs: The growing acceptance of cloud-native frameworks is poised to improve scalability and adaptability, allowing entities to efficiently utilize cloud resources. Recent statistics show that 66% of companies in the EU use the cloud for email management, while 53% utilize it for file storage, emphasizing a wider trend towards cloud adoption across different business functions.
Furthermore, 23% of organizations are running more than 5,000 containers, underscoring the scale of cloud-native adoption and its significance for ESB architecture.
AI and Machine Learning: The incorporation of AI capabilities into ESBs is set to transform data management by facilitating smarter routing, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making processes. This change not only enhances operational efficiency but also boosts the overall performance of unification systems.
Event-Driven Integration: A notable trend is the movement towards event-driven architectures, which facilitate real-time data processing. This method greatly enhances responsiveness to business changes, enabling companies to adjust rapidly to shifting market demands.
Low-Code Development: The rise of low-code platforms is simplifying ESB implementation, leading to faster development cycles and reducing the reliance on extensive coding expertise.
This democratization of development enables more teams within organizations to participate in collaborative projects, fostering innovation.
Enhanced Security Features: As system complexities increase, so does the demand for robust security measures within ESBs. Organizations are prioritizing data protection and compliance with regulations, ensuring that their connection solutions are not only effective but also secure.
These trends reflect a broader movement towards more agile, intelligent, and secure connection solutions, positioning ESB architecture as a cornerstone of modern enterprise design. The hybrid connection platform of the company illustrates how these trends are being tackled, especially in intricate and regulated sectors such as banking and healthcare. The name ‘Avato,’ derived from the Hungarian word for ‘of dedication,’ embodies the company’s commitment to architecting technology foundations that enable businesses to unlock isolated assets and create significant value.
Our group of specialists plays a crucial role in this process, ensuring that we deliver effective solutions customized to our clients’ needs. As noted by customer Gustavo Estrada, Avato simplifies complex projects and delivers results within desired time frames and budget constraints, showcasing its effectiveness in achieving integration goals swiftly and efficiently.
Conclusion
The integration of Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) architecture within organizations stands as a transformative force in enterprise technology. By enabling seamless communication among diverse applications, ESBs, such as Avato’s hybrid integration platform, significantly enhance operational efficiency, agility, and scalability. The key benefits—improved integration efficiency, reduced costs, and superior data management—empower organizations to respond swiftly to market demands, ultimately positioning them for success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
However, organizations must navigate common challenges associated with ESB implementation, including complexity, potential performance issues, and resistance to change. By adhering to best practices—such as defining clear objectives, embracing loose coupling, and planning for scalability—businesses can effectively design robust ESB architectures that not only meet current needs but also adapt to future demands.
Looking ahead, the future of ESB architecture is promising, driven by trends like cloud-native solutions, AI integration, and event-driven architectures. These innovations are set to further enhance the capabilities of ESBs, ensuring they remain integral to modern enterprise integration strategies. As organizations continue to leverage ESB technology, they will unlock significant value, streamline operations, and foster a collaborative environment that meets evolving business needs. Embracing ESB architecture is not merely a strategic choice; it is essential for organizations aiming to thrive in the digital age.

