Overview
The article emphasizes the imperative strategies and solutions required to achieve clinical interoperability in healthcare, a cornerstone for delivering effective patient-centered care. It underscores the necessity of adopting standardized protocols and investing in advanced integration solutions, such as Avato’s hybrid platform. Furthermore, fostering collaboration among stakeholders is crucial, as is addressing challenges like the lack of standardization and information privacy concerns. These efforts are essential to enhance data exchange and significantly improve patient outcomes.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare, clinical interoperability stands as a cornerstone for delivering high-quality, patient-centered care. This critical capability, defined as the ability of various healthcare systems and applications to seamlessly exchange and utilize data, is not merely a technological requirement; it is a vital driver for improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency. Yet, many healthcare organizations grapple with significant gaps in data exchange, often leaving clinicians without essential information at crucial moments.
As we approach 2025, the urgency to implement robust interoperability solutions becomes increasingly clear. Innovative platforms like Avato are leading the charge to bridge these gaps. Understanding the levels of interoperability, recognizing the challenges faced, and adopting strategic solutions are essential for healthcare providers. By enhancing care delivery, we can ensure that every patient receives the best possible treatment.
Are you prepared to tackle these challenges head-on? The time to act is now.
Define Clinical Interoperability and Its Importance
Clinical interoperability is the cornerstone of modern healthcare, enabling various medical information systems, devices, and applications to access, exchange, integrate, and collaboratively utilize data in a coordinated manner. This functionality is not just beneficial; it is essential for delivering high-quality, patient-centered care. By ensuring timely access to complete and accurate patient information, clinical interoperability significantly enhances care coordination, reduces the risk of medical errors, and improves the overall patient experience.
However, recent statistics reveal a pressing issue: only 42% of hospitals report that clinicians regularly use essential clinical information from external sources. This underscores a significant gap in information exchange that integration seeks to address. Tackling these integration issues is critical to ensuring clinical interoperability, allowing medical professionals to access comprehensive patient information. Moreover, as of 2022, only fifty percent of medical organizations conducted regular cybersecurity assessments, highlighting the urgent need for secure and dependable integration solutions, such as Avato’s hybrid integration platform, to protect sensitive information during exchanges.
By breaking down barriers between different networks, collaboration empowers medical professionals to make informed decisions based on thorough information. Avato’s dedicated hybrid integration platform simplifies complex integrations, maximizes the value of legacy systems, ensures 24/7 uptime and reliability, and provides real-time monitoring and alerts—features that are critical for sectors like banking, medical services, and government. This capability not only leads to improved health outcomes but also fosters operational efficiencies and reduces costs.
Continuous assessment of integration progress is vital; it guides future initiatives and analyzes policy effects within the healthcare sector. The case study titled ‘Measurement of Interoperability Progress’ illustrates the importance of monitoring achievements in this area, informing future initiatives effectively.
As we approach 2025, the significance of clinical interoperability for patient-centered care will only grow, necessitating robust integration solutions that can adapt to evolving needs. Expert opinions indicate that while frameworks like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) are emerging, their widespread deployment remains limited. An HIE representative noted, “We are just implementing our FHIR layer right now. What I will tell you is while FHIR is definitely a direction of the future, it is not broadly deployed in the marketplace and not broadly deployed in the workflow or business applications to great extent. But it is, definitely will be an important factor as we move into the future. But it also will not be the silver bullet that everybody’s hoping it was going to be.”
Therefore, organizations must prioritize the establishment of effective clinical interoperability solutions, such as those provided by Avato, to enhance care delivery and improve patient outcomes.
Explore Levels of Interoperability in Healthcare
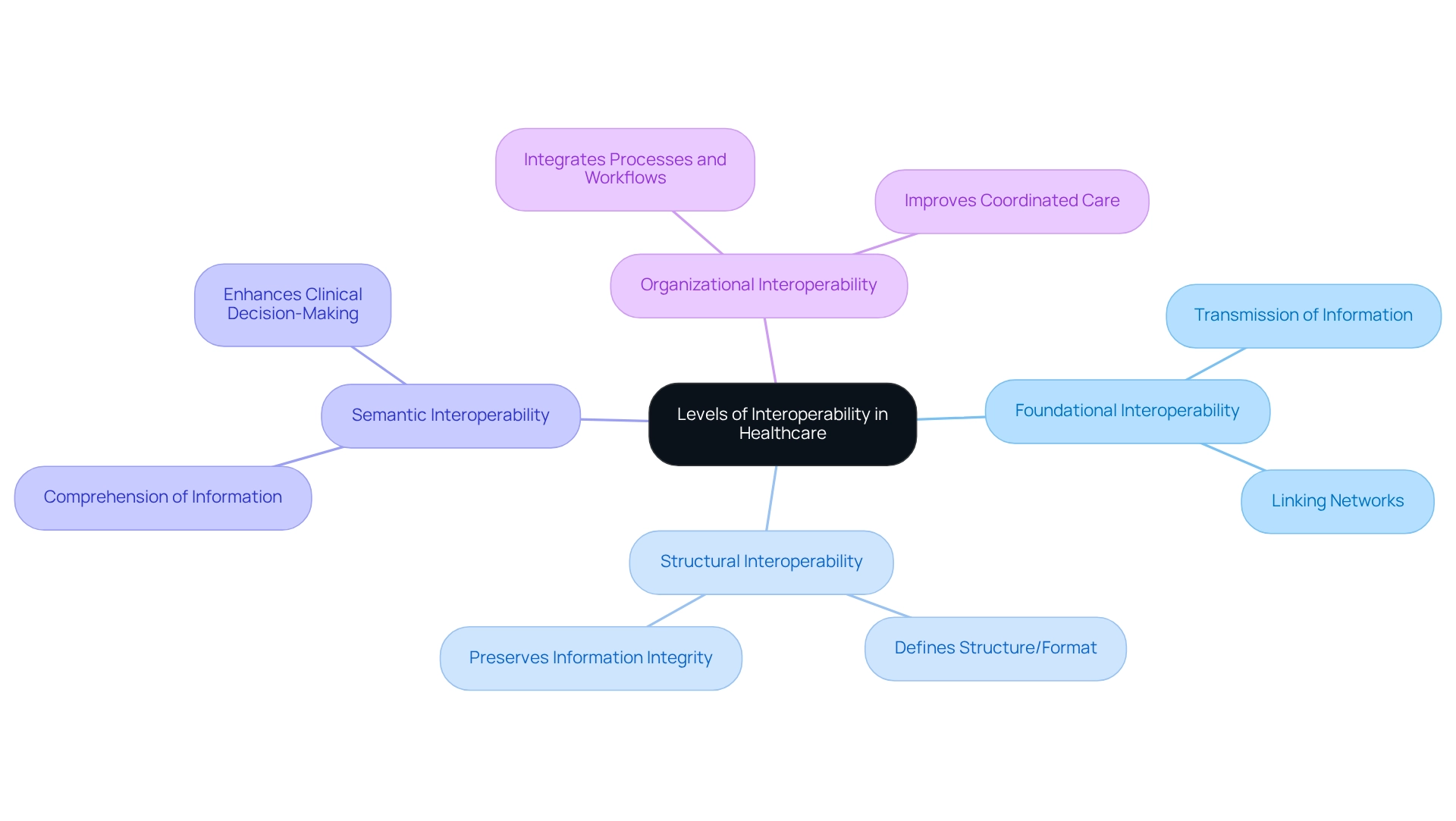
Clinical interoperability in healthcare is essential for effective information exchange and can be categorized into four primary levels: foundational, structural, semantic, and organizational.
Foundational Interoperability: This fundamental level allows one network to transmit information to another, ensuring that networks can link and communicate effectively. It serves as the groundwork for more advanced interoperability.
Structural Interoperability: This level defines the structure or format of the information exchanged, ensuring that the receiving entity can accurately interpret the details. It is essential for preserving information integrity during transfers.
Semantic Interoperability: At this level, both systems comprehend the significance of the information, enabling intricate exchanges and interpretations. This comprehension is essential for precise clinical decision-making and contributes to clinical interoperability by improving the usability of shared information.
Organizational Interoperability: The highest level involves integrating processes and workflows across organizations, enabling seamless collaboration and data sharing. This level of clinical interoperability is particularly important in the medical field, as it is essential for improving coordinated care and patient outcomes.
In 2023, a notable 22% of hospitals indicated they were not incorporating electronic health information, emphasizing the persistent difficulties in attaining effective integration. This statistic underscores the challenges healthcare organizations face in overcoming barriers to clinical interoperability. The greatest obstacle for digital health firms in the U.S. continues to be acquiring comprehensive patient information from external suppliers, which highlights the necessity for improved clinical interoperability and foundational connections.
Avato’s hybrid integration platform plays a crucial role in addressing these challenges by maximizing and extending the value of legacy infrastructures, simplifying complex integrations, and offering real-time monitoring. A significant illustration of successful integration is PaceMate’s remote cardiac monitoring solution, which demonstrates how a compatible system can enhance patient care. By optimizing data management, PaceMate establishes itself as a leader in remote monitoring, showcasing the tangible advantages of semantic integration in clinical environments.
As Robin Leahy, Vice President of Compliance, stated, ‘Clinical interoperability is already making a significant impact on the medical sector.’ Understanding these tiers of connectivity enables medical organizations to evaluate their existing capabilities and pinpoint areas for enhancement. As the medical landscape evolves, focusing on these levels will be essential for organizations aiming to enhance their integration strategies and ultimately improve patient care.
Implement Strategies for Achieving Interoperability
Healthcare organizations face the pressing challenge of achieving clinical interoperability.
- Adopt Standardized Protocols: Utilizing established standards such as HL7, FHIR, and IHE is crucial for ensuring compatibility between diverse systems. These protocols not only enhance information exchange reliability but also lead to a remarkable 40% increase in the reliability of machine learning algorithms for organizations that adopt standardized coding.
- Invest in Interoperability Solutions: Leveraging advanced integration platforms like Avato enables seamless data exchange and real-time monitoring, significantly reducing implementation time. Avato’s hybrid integration platform, supported by Red Hat’s JBoss Middleware, modernizes operations and enhances connected experiences, making it an ideal choice for healthcare settings. Notably, the national government has allocated $19 billion to promote health information technology, particularly electronic health records, underscoring the importance of investing in integration solutions that Avato provides through its enterprise architecture and project management services.
- Foster Collaboration: Promoting teamwork among stakeholders—including IT teams, clinicians, and administrative staff—aligns objectives and processes, which is essential for successful integration initiatives. This collaborative approach leads to more effective implementation of clinical practice guidelines through clinical interoperability. As demonstrated in the case study on tailored interventions for clinical practice guideline implementation, addressing specific barriers through collaboration is vital for overcoming challenges in clinical interoperability.
- Train Staff: Providing education for healthcare professionals on the importance of seamless communication and effective use of integrated frameworks is crucial. This education fosters positive changes in practice behaviors and enhances overall system utilization. Engaging staff in understanding the benefits of standardized protocols further supports successful adoption.
Furthermore, Avato emphasizes the necessity of essential strategies in staff training and change management to ensure smooth transitions to integrated systems.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously observing collaborative efforts and assessing their impact on patient care and operational efficiency enables organizations to make necessary adjustments. Utilizing robust analytics capabilities, as recommended by Avato, is critical for optimizing operations and improving customer experiences. This ongoing evaluation is essential for ensuring that integration initiatives achieve their intended objectives.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their integration capabilities, leading to improved patient outcomes and more efficient operations. Current trends indicate an increasing focus on integration solutions in 2025, making it imperative for medical organizations to stay ahead in this evolving landscape.
Identify Challenges and Solutions in Interoperability
Despite the evident advantages of interoperability, healthcare organizations frequently encounter significant challenges.
- Lack of Standardization: The variety in information formats across different systems complicates information exchange. Adopting universal standards and protocols is crucial for ensuring clinical interoperability and smooth information flow. The introduction of ICD-11, which features a chapter for traditional medicine, exemplifies efforts to standardize healthcare information, allowing for dual coding and enhanced integration of diverse medical practices.
- Information Privacy Concerns: Protecting patient information during exchanges presents a significant obstacle. Implementing strong security measures and adhering to regulations such as HIPAA is essential to mitigate risks related to breaches. Avato’s hybrid integration platform aims to improve data security while enabling seamless connectivity between different frameworks.
- Resistance to Change: Staff unwillingness to embrace new methods or processes can hinder progress. Comprehensive training programs that emphasize the advantages of system compatibility can facilitate smoother transitions and foster acceptance among staff. Avato emphasizes stakeholder engagement to ensure that all parties understand the value of new integration strategies.
- High Implementation Costs: The financial implications of upgrading systems can deter organizations from pursuing interoperability initiatives. Exploring funding opportunities and adopting phased implementation strategies can help distribute costs over time, making the transition more manageable. Avato’s dedication to architecting technology solutions allows organizations to future-proof their operations without overwhelming financial burdens.
In 2022, medical organizations reported heightened emphasis on cybersecurity risk mitigation, underscoring the significance of addressing privacy issues. Moreover, the introduction of ICD-11, which contains a chapter for traditional medicine, illustrates endeavors to standardize medical data, enabling dual coding and enhanced integration of various medical practices. As Gustavo Estrada noted, “Avato has the ability to simplify complex projects and deliver results within desired time frames and budget constraints,” emphasizing the importance of effective solutions in overcoming these challenges.
By proactively addressing these challenges, medical organizations can successfully execute integration initiatives that enhance clinical interoperability, ultimately improving patient care and operational efficiency. Additionally, implementation guides play a crucial role in applying standards to specific healthcare use cases, ensuring consistency and clarity in tackling interoperability challenges.
Conclusion
The journey toward achieving clinical interoperability is essential for enhancing the quality of patient-centered care. By defining interoperability and recognizing its significance, healthcare organizations can grasp the importance of seamless data exchange in improving care coordination and reducing medical errors. The four levels of interoperability—foundational, structural, semantic, and organizational—offer a framework for assessing current capabilities and identifying areas for improvement, highlighting the necessity for comprehensive strategies to bridge existing gaps.
Implementing standardized protocols, investing in advanced interoperability solutions, fostering collaboration among stakeholders, and providing thorough training for staff are critical steps for healthcare organizations. These strategies not only enhance interoperability capabilities but also lead to improved patient outcomes and streamlined operations. Addressing challenges such as lack of standardization, data privacy concerns, resistance to change, and high implementation costs is essential for successful integration efforts, ensuring that organizations can navigate the complexities of healthcare data exchange.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, the urgency to adopt robust interoperability solutions becomes increasingly apparent. Organizations that prioritize these initiatives will not only enhance care delivery but also position themselves as leaders in the pursuit of high-quality, patient-centered healthcare. The time to act is now; seizing the opportunity to improve interoperability will ultimately lead to better health outcomes for all patients.

