Overview
The article underscores the critical need for mastering healthcare interoperability software to facilitate seamless integration across diverse medical information systems. Effective interoperability is not just a technical requirement; it significantly enhances patient care, streamlines workflows, and reduces costs. However, challenges such as data silos and compliance concerns persist. Evidence shows that when implemented correctly, interoperability leads to improved patient outcomes and operational efficiencies. Are you ready to embrace this transformative technology? The integration platform is not merely an option; it is an essential step toward modernizing healthcare delivery.
Introduction
In an increasingly interconnected healthcare landscape, interoperability has emerged as a cornerstone for delivering efficient and effective patient care.
Healthcare interoperability refers to the ability of diverse information systems and devices to seamlessly exchange and utilize data. This capability is essential for enhancing care coordination and improving patient outcomes.
However, achieving true interoperability presents significant challenges, including:
- Data silos
- A lack of standards
- Privacy concerns
This article delves into the intricate world of healthcare interoperability, exploring its benefits, criteria for selecting the right software, implementation strategies, and troubleshooting common challenges.
By understanding these elements, healthcare organizations can navigate the complexities of interoperability more effectively, ultimately fostering a cohesive and efficient healthcare ecosystem.
Understand Healthcare Interoperability
Healthcare interoperability software is essential for enabling various information systems, devices, and applications to access, exchange, integrate, and collaboratively utilize information. This functionality is critical for medical providers, allowing them to share patient information seamlessly through healthcare interoperability software, which ultimately enhances care coordination and patient outcomes. Interoperability is categorized into four levels: foundational, structural, semantic, and organizational.
Each level plays a vital role in facilitating comprehensive information exchange and integration across diverse medical platforms. This categorization empowers organizations to assess their current healthcare interoperability software status and identify necessary enhancements.
Key Benefits of Interoperability
- Improved Patient Care: Access to complete patient histories enables healthcare providers to reduce errors and make informed treatment decisions, significantly impacting patient outcomes. Recent data indicates that 70% of hospitals involved in interoperable exchanges reported that clinicians frequently utilized clinical details from external providers when caring for patients. Furthermore, while most hospitals and primary care providers (PCPs) offer patient access to medical records through patient portals, the lack of unification across providers highlights a critical area for improvement in healthcare interoperability software.
- Enhanced Effectiveness: Healthcare interoperability software streamlines workflows by minimizing repetitive information entry and facilitating real-time information sharing, which is essential in dynamic medical environments. Avato’s hybrid integration platform exemplifies this efficiency, enabling organizations to unlock data and systems in weeks, not months, through its support for 12 levels of interface maturity.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating inefficiencies and enhancing resource allocation, healthcare interoperability software contributes to reducing operational expenses, allowing organizations to allocate funds more effectively.
Challenges to Interoperability
- Data Silos: Many healthcare organizations continue to operate with isolated systems that struggle to communicate effectively, impeding the flow of information.
- Lack of Standards: The absence of consistent information formats and protocols can obstruct effective information exchange, complicating interoperability efforts. The essential role of XML technologies in information transformation projects cannot be overstated, as they ensure healthcare interoperability software longevity and cost savings.
- Privacy Concerns: Ensuring data security and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA remains a top priority as organizations navigate the complexities of sharing sensitive patient information. A case study titled “Implementation Challenges in Health IT” illustrates that medical organizations face significant challenges due to the increasing number of health IT applications that overlap in functionality, complicating interoperability and cohesive patient experiences.
Understanding these concepts enables healthcare IT managers to navigate the complexities of selecting and implementing healthcare interoperability software, ultimately enhancing patient care and operational efficiency. As Gustavo Estrada from BC Provincial Health Services Authority noted, Avato simplifies complex projects and delivers results within desired time frames and budget constraints, showcasing the tangible benefits of effective interoperability solutions.
Define Selection Criteria for Interoperability Software
When selecting interoperability software, organizations should consider the following criteria:
-
Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the software adheres to industry standards such as HL7, FHIR, and DICOM, essential for facilitating seamless data exchange across diverse systems. Adherence to these standards is vital; research shows that registries requiring comparable information elements can attain nearly 80% coverage on average.
-
Security Features: Evaluate the software’s security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and adherence to regulations like HIPAA. These features are vital for protecting sensitive patient information, especially in a landscape where security breaches can have significant repercussions. High and highly variable error rates linked to MRA, varying from 70 to 2,784 mistakes per 10,000 fields, highlight the need for strong unification capabilities to reduce errors.
-
Scalability: Choose a solution that can grow with your organization, accommodating increasing data volumes and additional integrations as needed. A scalable platform for healthcare interoperability software ensures that your interoperability solution remains effective as your operational demands evolve.
-
User-Friendliness: The software should feature an intuitive interface that minimizes the learning curve for staff, thereby enhancing user adoption. A user-friendly design can significantly impact the efficiency of implementation and daily operations.
-
Integration Capabilities: Assess the software’s ability to integrate with existing systems, including Electronic Health Records (EHRs), billing systems, and other healthcare applications. Avato’s hybrid unification platform excels in this area, enabling organizations to maximize and extend the value of legacy systems while simplifying complex connections. Efficient unification abilities provided by healthcare interoperability software are crucial for establishing a connected medical ecosystem. For instance, Media’s role in HL7 and DICOM integration illustrates how cloud-based solutions can improve collaboration and streamline workflows, enabling providers to unlock the full potential of these standards.
-
Vendor Support and Training: Consider the level of support and training provided by the vendor to ensure successful implementation and ongoing maintenance. As Gustavo Estrada noted, “Aviator has the ability to simplify complex projects and deliver results within desired time frames and budget constraints.” Strong vendor support can facilitate smoother transitions and help organizations navigate challenges during and after deployment.
By establishing these criteria, organizations can systematically evaluate potential interoperability solutions, ensuring they select the one that aligns best with their operational needs and strategic goals.
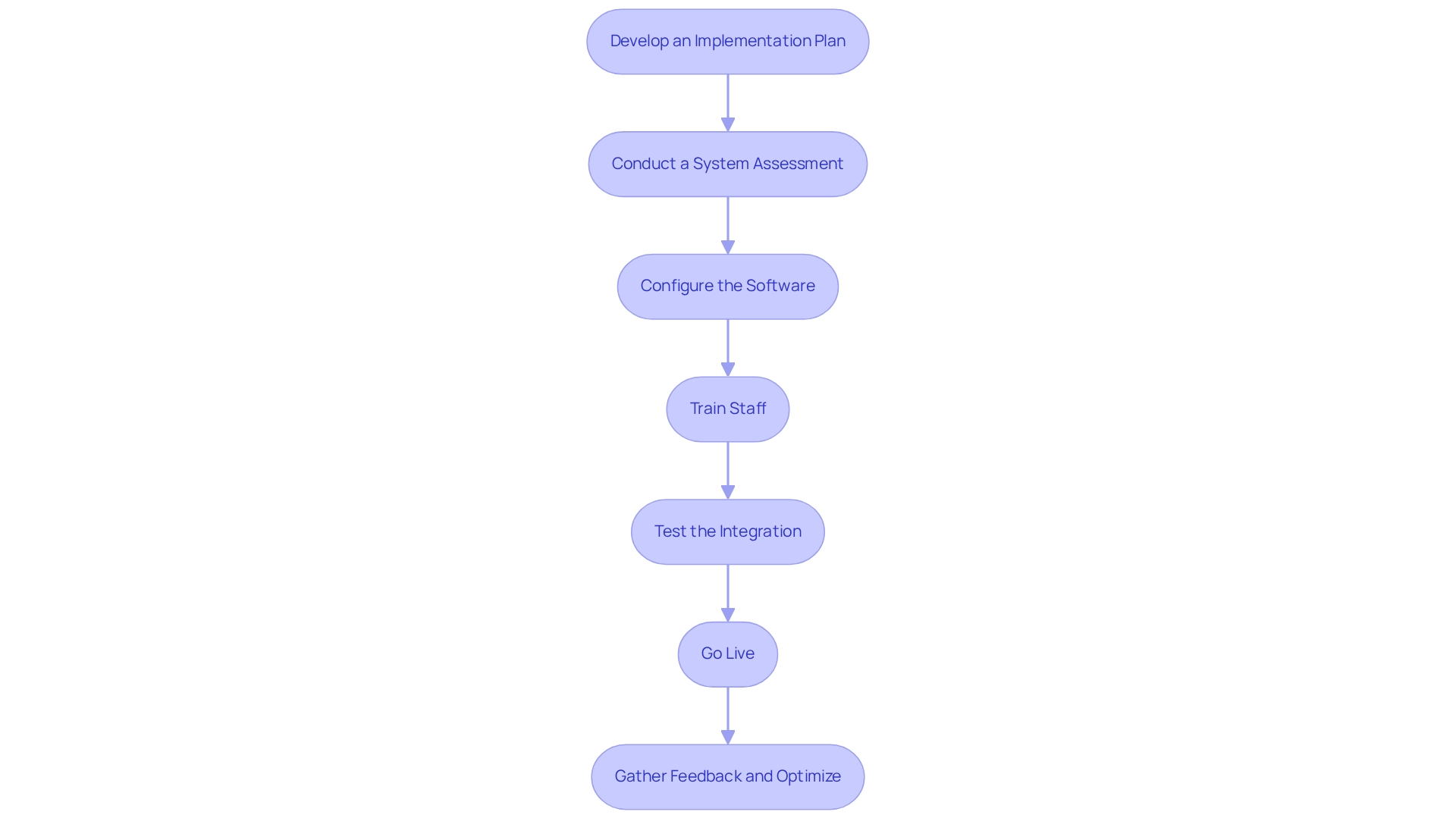
Implement the Selected Interoperability Software
To successfully implement interoperability software, adhere to the following steps:
- Develop an Implementation Plan: Craft a comprehensive plan detailing the timeline, resources, and key milestones for the implementation process. Engage all relevant stakeholders, including IT staff, healthcare providers, and administrative personnel, to ensure alignment and support.
- Conduct a System Assessment: Perform a thorough evaluation of existing systems and workflows to pinpoint integration opportunities and potential challenges. This assessment is crucial for tailoring the implementation strategy to meet your organization’s unique requirements.
- Configure the Software: Customize the software settings to align with your organization’s workflows and data management practices. Clearly define all essential mappings and transformations to facilitate seamless integration. Utilizing XSLT can greatly improve this process by streamlining XML conversions and minimizing programming errors, ultimately resulting in cost savings.
- Train Staff: Deliver extensive training for all users to ensure effective utilization of the new software. This training should cover both technical aspects and best practices for information entry and management, fostering a culture of competence and confidence. Emphasizing the importance of schemas during training can further reduce errors and enhance data management efficiency.
- Test the Integration: Conduct rigorous testing of the software to identify and rectify any issues prior to going live. This should include functional testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing to ensure the system meets operational standards.
- Go Live: After successful testing and resolution of any identified issues, launch the software. Monitor the system closely during the initial phase to swiftly address any unforeseen challenges that may arise.
- Gather Feedback and Optimize: Post-implementation, actively solicit feedback from users to identify areas for enhancement. Utilize this feedback to refine the system configuration and enhance the overall user experience.
By following these steps, organizations can achieve a successful implementation of interoperability software, significantly enhancing information sharing capabilities and improving patient care results. The European Health Information Space Initiative exemplifies this approach, facilitating cross-border health information exchange and enhancing healthcare delivery across EU member states. This initiative supports member states in their digital health transformation, enhancing citizens’ access to their health data.
Furthermore, according to research that included 85 relevant articles, the importance of a reliable and future-proof technology stack cannot be overstated. As Gustavo Estrada pointed out, ‘Avato has the capability to simplify intricate projects and provide outcomes within preferred time frames and budget limitations,’ emphasizing the importance of choosing a strong platform for interoperability solutions.
Troubleshoot Implementation Challenges
During the execution of healthcare interoperability software, organizations frequently encounter multiple challenges that can hinder effective unification. Understanding these challenges is crucial for successful integration. Below are common issues along with strategic troubleshooting solutions:
- Data Inconsistencies
Issue: Discrepancies in data formats or missing data can significantly hinder integration efforts. Statistics indicate that 68% of medical projects utilize HL7 standards, yet inconsistencies remain prevalent.
Solution: Conduct a comprehensive mapping exercise prior to implementation to ensure uniformity across information sets. Post-implementation audits are crucial for identifying and rectifying any inconsistencies that may arise. The complexity of healthcare data management, as highlighted in case studies, underscores the necessity for sophisticated tools to navigate these challenges effectively. - Integration Failures
Issue: Compatibility issues may prevent the software from connecting with existing systems, leading to integration failures.
Solution: Ensure that all systems meet the necessary technical specifications for incorporation. Work together with the vendor to tackle and solve any compatibility issues that arise. Avato’s hybrid unification platform is designed to accelerate secure system unification, particularly in sectors like banking and healthcare, ensuring a robust connection between legacy systems and new technologies. - User Resistance
Issue: Staff may resist adopting new software due to unfamiliarity or perceived complexity, which can stall integration efforts.
Solution: Implement ongoing training and support initiatives to build user confidence. Clearly communicate the benefits of the new system to foster acceptance and encourage buy-in from all stakeholders. Engaging stakeholders early in the process is crucial, as Avatar emphasizes the importance of mobilizing them to get requirements right the first time around. - Performance Issues
Issue: Slow performance or unexpected downtime can disrupt operations and affect user experience.
Solution: Monitor system performance rigorously and collaborate with the vendor to optimize configurations. Ensure that the infrastructure is robust enough to support the software’s operational demands. Avato’s architecture is designed for collaboration projects requiring 24/7 uptime, minimizing the risk of defects or outages. - Compliance Concerns
Issue: Maintaining compliance with regulatory standards during integration can be challenging for organizations.
Solution: Regularly review compliance requirements and ensure that the system adheres to all relevant regulations. Involve legal and compliance teams throughout the implementation process to mitigate risks.
By proactively tackling these challenges, organizations can greatly improve the efficiency of their healthcare interoperability software, resulting in a more seamless merging process and better health results. As Gustavo Estrada noted, “Avato has the ability to simplify complex projects and deliver results within desired time frames and budget constraints,” emphasizing the importance of effective interoperability solutions. Additionally, the future of healthcare data management will likely include more sources, such as patient-generated data from devices like fitness monitors and blood pressure sensors, further complicating integration efforts and highlighting the need for adaptable solutions.
Conclusion
Achieving healthcare interoperability transcends mere technical necessity; it represents a transformative leap towards enhancing patient care, improving operational efficiency, and reducing costs. By grasping the essential aspects of interoperability—its levels, benefits, and challenges—healthcare organizations can strategically position themselves to navigate this intricate landscape. The key benefits, including improved patient care and streamlined workflows, highlight the critical need for robust interoperability solutions.
The processes of selecting and implementing interoperability software are paramount, requiring careful consideration of compliance, security, scalability, and user-friendliness. Establishing clear criteria for evaluating potential solutions ensures that organizations choose software tailored to their unique operational needs. Moreover, a well-structured implementation plan, paired with comprehensive training and ongoing support, is crucial for overcoming common challenges and maximizing interoperability benefits.
As the healthcare sector evolves, the integration of diverse data sources will become increasingly vital. Organizations must proactively tackle potential hurdles, ranging from data inconsistencies to compliance concerns, to secure successful interoperability. By cultivating a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement, healthcare providers can harness technology to forge a cohesive ecosystem that ultimately elevates patient care and outcomes. Embracing interoperability is not merely an option; it is a strategic imperative that will shape the future of healthcare delivery and enhance patient experiences.

